* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
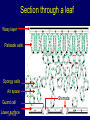
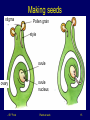
Plants at work J E F Frost Plants at work 1 Plants are producers Plants get their energy from light Plants make food by photosynthesis Light energy is trapped by chlorophyll Most of the food is stored as starch J E F Frost Plants at work 2 Photosynthesis Word equation sunlight Carbon dioxide + water chlorophyll sugar + oxygen Plants make new biomass during photosynthesis J E F Frost Plants at work 3 Leaves Leaves are green because they contain chlorophyll Leaves have a large surface area to absorb as much light as possible J E F Frost Plants at work 4 Testing for starch Iodine changes from brown to blue-black where there is starch Method Soften the leaf with boiling water Remove the green colour with ethanol Add drops of iodine Look for the colour change! J E F Frost Plants at work 5 Variegated leaves Some leaves are not green all over Some have white and green stripes or patches Only the green parts will contain starch Why? J E F Frost Plants at work 6 Respiration in plants All living things carry out respiration Leaves are thin so that gases can get in and out easily Gases get into and out of leaves through little holes called stomata J E F Frost Plants at work 7 Section through a leaf Waxy layer Palisade cells Spongy cells Air space Stomata Guard cell Lower surface J E F Frost Plants at work 8 Plant growth •Plants need carbon dioxide from the air •Plants need water •Plants need light •Plants need nutrients from the soil including nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium •If the soil does not contain enough nutrients then we add fertilisers J E F Frost Plants at work 9 Fertilisers Nitrogen is needed for general growth Phosphorus is needed for healthy roots Potassium is needed for healthy leaves J E F Frost Plants at work 10 Plant plumbing Water and minerals enter the plant through the roots Then they go up through little tubes called xylem in the plant stem Food is transported through tiny tubes in the stem called phloem J E F Frost Plants at work 11 Roots Roots keep the plant anchored in the soil Roots are covered in lots of tiny hairs Root hairs take up water from the soil All the root hairs together have a large surface area J E F Frost Plants at work 12 Flowers Flowers are a plant’s reproductive system Flowers have male and female reproductive organs Male part (stamen): anther and filament Female part (carpel): stigma, style, ovary J E F Frost Plants at work 13 Pollination Pollination is the transfer of pollen (male) to the stigma (female) Pollen grains can be carried by insects Pollen grains can be carried by the wind When the ovule is fertilised it turns into a seed J E F Frost Plants at work 14 Making seeds stigma Pollen grain style ovule ovary J E F Frost ovule nucleus Plants at work 15 Key words plant seed root stem leaf root hair starch J E F Frost chlorophyll photosynthesis carbon dioxide oxygen phosphorus nitrogen potassium Plants at work pollen anther filament stigma style ovule xylem phloem 16