* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Layers of the Atmosphere
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
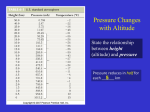
Ranges from 0 km to 12 km Lowest layer of the atmosphere Where we live Where almost all of the Earth’s weather weather occurs “Tropo” means turning or changing; named because conditions are always changing Shallowest layer of the atmosphere with almost all of the mass of the entire atmosphere… How is this possible? It is the most dense because gravity pull the molecules towards the surface. As altitude increases, temperature drops. Why? Because the air gets less dense as altitude increases. (fewer molecules to trap in the heat) Ranges from 12 km to 50 km “Strato” means layer or spreading out The ozone layer is located in the upper stratosphere, and it protects the Earth by absorbing and filtering out the sun’s harmful U-V rays. As altitude increases, temperature increases. Why? The upper stratosphere contains the ozone layer which absorbs energy and turns it into heat causing the temperature to be greater in the upper stratosphere. Ranges from 50 km to 80 km Middle layer of the atmosphere “Meso” means middle protects the Earth from most meteors As altitude increases, temperature drops. Why? The lower mesosphere is closer to the ozone layer (hot) and the air gets less dense with altitude so it gets colder. Ranges from 80 km and beyond very thin air “Thermo” means heat Broken into 2 layers- The Ionosphere and the Exosphere As altitude increases, temperature increases. Why? Although the air is very thin, the molecules are the first to receive energy from the sun, so the molecules are very hot. Is the lower portion of the Thermosphere Ranges from 80 km to 550 km where gas molecules become electrically charged particles called ions Radio waves bounce off ions and back to Earth Where the Aurora borealis is found (Northern Lights) Is the outer portion of the Thermosphere Ranges from 550 km to outer space “Exo” means outer satellites orbit here Temperature decrease. The air gets less dense as altitude increases. There are less molecules to hold heat. Temperature increases. The ozone layer is found at the top of the stratosphere. The ozone layer holds in heat, so as altitude increases temp. increases. Temperature decreases. The bottom of the mesosphere starts out warm because of the ozone layer. As altitude increases, there are less air molecules to hold heat. Temperature increases. This layer is the closest to the sun. The air molecules receive the heat from the sun.