* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Extinction debt wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Great American Interchange wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
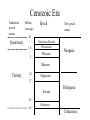
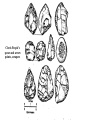
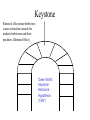
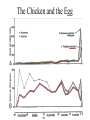
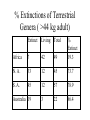
Check updated study questions and help file on calculating background rates of extinction. Exam Resources Section Cenozoic Era Traditional period names Million Epoch years ago New period names .01 Quaternary 1.8 5 Holocene (Recent) Pleistocene Pliocene Neogene Miocene Tertiary 24 Oligocene 37 Eocene Paleogene 58 65 Paleocene Cretaceous American Pleistocene Extinctions • 135 species of large mammals went extinct in N. and S. America about 11,000 years ago. • Why? – Climate change – Human mediated Early Sites in the Americas • Clovis People expand into the Americas • 15,000 years ago • Maybe 20-40,000 years ago http://www.sciam.com/2000/0900issue/0900nemecekbox2.html Clovis People’s spear and arrow points, scrapers Human Predation • Overkill Hypothesis – Archeological evidence of hunting tools – Arrow points etc. embedded in fossilized bones • Blitzkrieg – Naïve predators or ineffective defenses New World Blitzkrieg? But . . . Predator-Prey Theory? Prey Density Predator switches to more common prey Prey is maintained at low density Time Mammoth Hunter . . . or Fish Catcher? http://www.sciam.com/2000/0900issue/0900nemecek.html Human-Mediated Extinction • Predation – Overkill – Blitzkrieg • Disease • Fire Human Rats http://www.sciam.com/interview/2001/010201macphee/index.html Gradual Extinctions? Climate-Change Hypothesis • ME took place during the last glacial retreat 10 to 11,000 years ago. • Less savanna and grasslands, and more deciduous forests and swamp environments. • Hypothesis: Mega-herbivores went extinct and destabilized communities. The whole pyramid tumbled. Evidence Against • No large-scale extinctions of megavertebrates for previous glacial retreats. • More extinctions expected in areas most affected by climate change – north of N.A. and tropics of S.A Interaction of Hunting and Climate Change • Mega-herbivores as “ecosystem engineers” – Keystone Herbivore Hypothesis • Domino Extinctions Keystone Removal of keystone herbivores causes extinction cascade for midsize herbivores and their predators (Domino Effect) Owen-Smith: Keystone Herbivore Hypothesis (1987) The Chicken and the Egg Large mammals selected against: Taxa of South American land mammals Large and small species Existing before man’s arrival Genera: 153 Extinct 10,000 years ago Large-bodied species 56 54 96% Pleistocene Survivors - I • Holarctic Distribution – grizzly bear, moose, elk, wolves, musk-oxen • But . . . – llama, tapirs, prong-horn antelope, mountain goat Pleistocene Survivors - II • Susceptibility to environmental change – Grizzly bears vs. sabre-toothed tigers • Vulnerability to human hunters – Mountain goat vs. woolly mammoth % Extinctions of Terrestrial Genera ( >44 kg adult) Extinct Living Total Africa 7 42 49 % Extinct 19.3 N. A. 33 12 45 73.7 S. A. 45 12 57 78.9 3 22 86.4 Australia 19 What About Africa? • Human history? • Climate change? • Equivocal evidence