* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
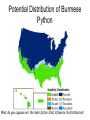
Ecology the study of the interaction of organisms with one another and with the environment. Themes in Ecology • • • • Energy Transfer Biodiversity Ecosystem Change Organism Interactions Distribution • is the range of places that a species inhabits Burmese Python Why is the Burmese Python a Problem? Hypothetical Diet for a Python to reach 13 ft. Distribution • Distribution for a species is governed by: – Biotic Factors - parts of the environment that affects living organisms. • Predation, Algal blooms, food supply, blights, territory. – Abiotic Factors - non-living part of the environment that affects living organisms • Temperature, Water, light, soil pH (acidity), salinity, and mineral nutrients. Potential Distribution of Burmese Python What do you suppose are the main factors that influence its distribution? Ecological Niches • Studies of the distribution and interaction of organisms show that there are many different ways to exist in an ecosystem. • The mode of existence by an organism in an ecosystem is referred to as an ecological niche. A niche includes: – Habitat – where the species lives – Nutrition – how the species obtains food – Relationships – the interaction with other species. Food Web The actual niche is usually smaller than the potential niche • It’s limited by biotic and abiotic factors – limiting factors Competition Exclusion Principle • Two organisms occupying the same niche will compete; only one species can occupy that niche. Food Pyramid • Producers • Decomposers • Consumers – Herbivore – Carnivore – Omnivore Why Save the Reefs • Economic Reasons – – new commodities such as medicines or materials. – Ecotourism can provide a lot of $$$. • Ecological Reasons – – Reefs buffer large amounts of carbon dioxide. – Damage to reefs could have broad effects on other ecosystems • Ethical Reasons – Every species has a right to life. – Reefs have cultural importance to indigenous human populations. – It would be wrong to deprive future humans of the resource. • Aesthetic Reasons – Reefs have natural beauty that give us enjoyment. – Reefs inspire people.