* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap. 16 Ecosystems
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Mission blue butterfly habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
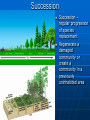
Chap. 16 Ecosystems What is an Ecosystem? Section 1 Interactions of Organisms and Their Environment Ecology – the study of the interactions of living organisms with one another and with their physical environment Habitat – the place where a particular population of a species lives Levels of Organization Organism – an individual living thing Population – a group of the same species that lives in one area Community – the many different species that live together in a habitat Ecosystem or ecological system – consists of a community and all the physical aspects of its habitat – complex web of connected biotic & abiotic factors Biome – a major regional or global community of organisms Keystone species Is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem Form and maintain a complex web of life Affects all the other species connected to it Biosphere – living globe – that part of the Earth in which life exists Extends to as far as 8 kilometers above the Earth’s surface to as far as 8 kilometers below the surface of the ocean Organisms are not distributed uniformly throughout the biosphere Factors of An Habitat Abiotic factors – physical aspects of a habitat – natural nonliving Biotic factors – the organisms in a habitat Physical Aspects Terrain Water Soil • Minerals • Composition • Organic matter • pH Air atmosphere Weather/climate Intensity of sunlight Diverse Communities in Ecosystems Biodiversity – the variety of organisms, their genetic differences, and the communities & ecosystems in which they occur Ecosystem Inhabitants of a Pine forest Which of the six kingdoms of organisms would be represented if you fenced a square kilometer of the forest? Ecosystem Boundaries Physical boundaries of an ecosystem are not always obvious, also depends of ecosystem being studied Change of Ecosystems over Time Pioneer species – the first organisms to live in a new habitat where soil is present Tend to be small, fast-growing plants examples: lichen, mosses – can break down solid rock into smaller pieces Make the ground more hospitable for other species Succession Succession – regular progression of species replacement Regenerate a damaged community or create a community in a previously uninhabited area Primary succession – occurs where life has not existed before Secondary succession – occurs in areas where there has been previous growth Reestablishment of a damaged ecosystem Small disturbances start the process Again & again Climax Community which populations of plants or animals remain stable and exist in balance with each other and their environment. A climax community is the final stage of succession, remaining relatively unchanged until destroyed by an event such as fire or human interference http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078802849/student_ view0/unit1/chapter3/concepts_in_m otion.html# Pond Succession http://www.sabah.ed u.my/csm07010/Form %204/pond.htm Pond succession occurs due to the change in depth of the pond. When submerge plants die, it will deposit at the bottom of pond. Over the time, the pond becomes shallow until finally filled in.