* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Primary productivity
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
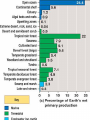
Primary Productivity Amount of energy or mass created during photosynthesis gC/m2/yr or kcal/m2/yr Net Primary Productivity: biomass for herbivores GPP – CR = NPP Factors that contribute to its success Nutrients, temperature, sunlight, moisture Primary Productivity Factors that contribute to its success Nutrients, temperature, sunlight, moisture Nutrients as limiting factor P = freshwater N = terrestrial + marine Ecosystems are stable, resilient, and resistant Stable: self perpetuating Ecosystems are stable, resilient, and resistant Resilient : repair itself If a tree has been damaged it can regrow using suckers Ecosystems are stable, resilient, and resistant Resistant: ability to protect itself Secondary Succession: soil is there. Change is natural PRIMARY: NO SOIL SECONDARY: STARTS WITH SOIL MICROCLIMATE Lichen are pioneer species YELLOWSTONE- 1988 700,000 aces burn for 2 months Changed the structure of the ecosystem. Stable ecosystems are resilient to change DID THE YELLOWSTONE WILDFIRE AFFECT THE ABUNDANCE OR DIVERSITY OF ORGANISMS? HOW DOES THE SELECTIVE PRESSURES CHANGE? Abundance of shade tolerant species decrease Abundance of shade intolerant species increased Diversity remained the same. Disturbance adapted species: Prairies Deep roots Forests Serrotinous cones Ecological Succession Primary Succession - A community begins to develop on a site previously unoccupied by living organisms. Example: A lava flow creates a new land area that is colonized. The first colonists are termed pioneer species. Secondary Succession - an existing community is disrupted and a new one subsequently develops at the site Climax community - community that develops last and remains the longest A disturbance is any force that disrupts established patterns of species diversity and abundance, community structure, or community properties e.g. storms, fires, logging. Disturbance tends to disrupt the superior competitors the most and allows less competitive species to persist. Some landscapes never reach a climax community because they are characterized by periodic disturbances (such as wildfires) and are made up of disturbance-adapted species.