* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Traits of Life PPT
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
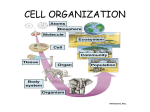
Introduction to Biology Spring 2015 Essential Question •What are the traits that make something alive? Biology • Bio-: life • -logy: study of • Biology: study of living thing • Living things are called organisms. Living things are called organisms. 1. There are 21 organisms in the graphic. 2. Can you find them? 1) There are 21 organisms in the graphic. 2) Can you find them? Spirogyra Paramecium Amoeba Bacteria Volvox Living things are called organisms. 1. Arrange them in 5 groups. 2. Name each group. 5 Kingdoms of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Eubacteria Archaea Bacteria TRAITS OF LIFE What are some traits that ALL living things share? 1. 2. 3. 4. All species reproduce. All living things grow and develop. All living things obtain and use energy. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 5. All living things respond to stimuli. 6. All living things maintain an internal balance. What are some traits that ALL living things share? GO BACK AND COMPARE THE ORIGINAL LIST TO THE 6 TRAITS WE JUST LEARNED. Which were the same? Different? Why? Trait #1 All species reproduce. (Doesn’t have to be every single organism in that species) True or False? Reproduction requires two organisms. FALSE! ONE bacteria can split into two! A hydra “buds” to make another. And if you cut a starfish in half it will regenerate into TWO starfish! These are examples of ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION. • Asexual Reproduction: one parent creates a new organism with identical genetic information (NO sperm or egg) – A-: not – -sexual: involving two parents Budding Binary Fission True or False? Sexual reproduction requires sexual intercourse. FALSE! This is a sea urchin… Sea urchins release sperm and egg into the water. Sexual Reproduction: two parents create a new organism by combining their genetic material (usually via sperm and egg) With asexual reproduction offspring will inherit the same exact traits as their parents. With sexual reproduction, offspring will differ from their parents in some ways because they will be inheriting DNA from both the sperm and egg. Trait #2 All living things grow and develop. Growth is getting larger as cells divide to form more cells. Development is change in form or function. Embryonic Stem Cells Development Trait #3 All living things get energy and use energy. The _____ is the primary source of energy for almost everything on Earth. How does each of these organisms GET energy? And how do they USE energy? Autotroph: An organism that uses light or chemicals to make its own food (PHOTOSYNTHESIS). Heterotroph: An organism that eats other organisms to obtain energy. • Energy from food must be broken down during chemical reactions into a form that cells can use (CELLULAR RESPIRATION). Trait #4 All living things are made of one or more cells. Just like a house is made of bricks… Organisms are made of cells… Unicellular Organisms • Unicellular: single-celled organism – Uni-: one – -cellular: made up of cells – Ex.: bacteria and protists bacteria protists Multicellular Organisms • Multicellular: organism made up of 2 or more cells – Multi-: many, several – Ex.: plants, animals, fungi plants animals fungi Unicellular or Multicellular? A B Trait #5 All living things respond to stimuli. Response to Stimuli • A stimulus is anything that causes a response in an organism. • What is the stimulus? • Stimuli can be • What is the internal or external. response? • Ex: A pupil gets • How is this helpful? smaller in bright light. A Venus fly-trap closes when a fly lands on it. • What is the stimulus? • What is the response? • How does this help it? Trait #6 All living things maintain internal balance (HOMEOSTASIS) (of things like water, sugar, temperature). Homeostasis If body temperature drops too low, shivering produces heat to warm you up. If temperature is too hot, sweating cools you down. What internal condition is out of balance in these photos? What is the stimulus? How will the body respond? not enough too much The chart shows four levels organisms. Which statement correctly describes a level of organization in the human nervous system? a. b. c. d. Nerve cells group to form nerve tissue. The brain is a group of nervous systems. The organs of the nervous system form a nerve cell. The nervous system has two groups of nerve tissues. Because no organism lives forever, __________ is necessary in order to prevent extinction of a species. a. b. c. d. Development Growth Homeostasis reproduction Which characteristic is shared by all eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control cell processes c. Use of cellular respiration for energy release d. Ability to move in response to environmental stimuli LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Levels of Organization •Atoms smallest •Molecules •Organelles •Cells •Tissues •Organs All of the organelles function inside the cell just •Organ System •Organism largest like organs function within our bodies. Atoms In atoms, the outer shell of electrons, also called valence electrons, likes to be full with 8 electrons, oxygen only has 6 Molecules Two types of atoms can combine together to forms a molecule so that every atom has a full valance of electrons. Organelles Organelles make up cells and all have a very specific function. Cells Cells: the building blocks of life Ex: An individual neuron is a type of cell that is differentiated for a specific function in the brain. Tissues Tissues: Several of the same types of cells working together to create tissue Tissues (nerve tissue) Organs Groups of tissues form organs. Organ (brain) Organ Systems •Organs that work together to perform a similar function are called an organ system. • Ex: The digestive system allows us to break down food into smaller parts that our body can use. Organisms Organism: an individual living thing Levels of Organization •Organisms are grouped even further into the following smallest categories: –Populations –Communities –Ecosystems –Biosphere largest Populations •Population: a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time. Community Community: all of the populations of different species in the same place at the same time. Ecosystem •Ecosystem: living organisms that interact with each other and the abiotic factors in a given area –Biotic: living things. •Ex: plants and animals –Abiotic: non-living things. Ex: temperature, climate, soil, rocks. Biosphere •Biosphere: the life-supporting portion of Earth. 64 Which of these would form first during the development of a complex multicellular organism, such as an animal? a. b. c. d. Cell Organ Tissue Organ system The picture shows a group of muscle cells in the heart. All of these muscle cells beat in unison to push blood in timing with the rhythm of the heart, at the direction of nearby nerve cells. These muscle cells could best be called a a. Organ b. Tissue c. Macromolecule d. Organ system Based on the organization of living things, how could we classify the pollen produced by this flower? a. An organ that is part of a system b. A group of cells that form an organ c. Begins as a cell and is part of a system without organs d. Begins as a cell, come from an organ, is part of a system