* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
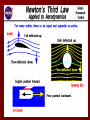
Force A push or pull exerted on an object. Forces… Forces are vectors – Have both magnitude and directions Net Force – Vector sum of all forces acting on a body When the net force on an object is zero, the object is in equilibrium – In otherwords, the acceleration is zero. Force & Motion Forces cause accelerations – Change in velocity Speed and/or direction Consider the book on the table. In order for the book to move, an unbalanced force has to act on the book. Systems When considering how a force affects motion, it is important to identify the object of interest. This object is called the system. Everything around the object that exerts forces on it is called the external world. The identifiable cause is called an agent. Contact Forces • A contact force exists when an object from the external world touches a system and thereby exerts a force on it. Friction Tension Normal Applied Field Forces Field forces are exerted without contact. – Also known as non contact forces or action at distances forces Gravitational Electrical Magnetic Free Body Diagram Free Body Diagram: a physical model that shows all the forces acting on the system. Each force is drawn as a vector leading away from the object. *Must be drawn for every problem FBD Example A car accelerating to the right experiencing friction. Normal Applied Friction Weight Newton’s First Law An object in motion, stays in motion; an object at rest stays at rest unless acted on by a net force. Also known as the law of inertia!!! Inertia… Inertia An object’s resistance to change its state of motion. An object’s mass is a measurement of the object’s inertia. – The more mass an object has, the more resistance it will have to change its state of motion. Mass vs. Weight Mass – – – – Amount of matter present in an object Constant – same everywhere in the universe A measurement of an object’s inertia Measured using a BALANCE Weight – – – – Force due to gravity W = mg Changes as the acceleration due to gravity changes Measured using a SCALE Newton’s nd 2 Law Acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass. F = force – Measured in Newtons m = mass – Measured in kilograms a = acceleration – Measured in m/s2 Newton’s rd 3 Law For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. Interactions All forces result from interactions between objects. Action-Reaction force pairs act on different objects. – Action-Reaction forces do NOT cancel out because they act on different objects.