* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4000 N/C
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
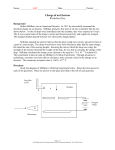
Think • We calculated the force of gravity for 2 electrons to be much much smaller than the electrostatic force between these two electrons. Would it be possible for a charged object to have an equal force due to gravity (downwards) and an electrostatic force pushing upwards? Explain ! Test Tomorrow ! • Wondering why you did not get in the 90’s on the last quiz? • Think back to how seriously you did the homework. • Make sure you review/do the homework assignments before the test. They should all be open. Study- make sure they make sense. Today • Review by looking at a topic that combines several ideas. Make sure you are asking questions if it does not make sense !! • HW – Castle Learning – Electrostatic Review (and ALL unfinished homeworks) Millikan’s Idea • Robert Millikan was a scientist who studied electricity. • During the early 1900’s, scientists thought of electricity as a fluid. • They had the concept of CHARGE, but not of ELECTRONS! • Millikan set about to find out if there were ‘bits’ of charge Things Millikan Knew • Acceleration due to gravity • An object with a net force of 0 moves with a constant velocity • Droplets can be charged using x-ray’s • “Stokes’ Theorem” – mass of droplets • How to find the electric field between two plates Millikan’s Apparatus Millikan sprayed oil droplets into a chamber with charged plates at the top and bottom The droplets come out with a CHARGE on them They areThey attracted to one plate or the other are attracted to one plate or the other depending on their charge! Millikan’s Apparatus Millikan noticed that when he adjusted the electric field, some of the droplets would not move UP or DOWN. WHY??? Fg must be equal to Fe forces on an object WhatWhat do we knowact about these twoinforces? gravitational and electric fields? Equations Millikan looked at this using the equations: Fe Eq Fg mg He noted that droplets only stopped moving when the electric field was set to certain strengths. Eq mg mg q E What does this suggest? Electrical “Bits” • Millikan did many observations, collecting thousands of data samples for charge on oil droplets. • This experiment has been repeated by hundreds of physicists (and university physics students) with the same results. • Charge ONLY occurs in multiples of 1.6 x 10-19C • A +5.0 coulomb charge is located in a uniform electric field of intensity 4000 newtons per coulomb. Calculate the force on the object. E = 4000 N/C + 5.0 C F = Eq F = (4000 N/C)(+5.0 C) = 20,000 N • Which of the following is a correct drawing of the field lines near a negatively charged object? a b c d b. Field lines pointing INWARD - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + + + + + + + + + + + + + + • A proton is placed between two equal, but oppositely charged plates. What will happen to the proton? + The proton will ACCELERATE toward the negative plate! The electric field between the plates provides a constant, unbalanced FORCE on the proton • At which point is the electric field intensity ZERO? A + 2.0 C B + 2.0 C At point B. The midpoint between two like charges experiences no ‘net field’ – the fields of the like charges cancel out in that area. • In which direction will the electric field between the plates point? + + + + + + + + + + + + + + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Field lines always point from the positive plate to the negative plate. • An object with a charge of -0.45 coulombs experiences a force of 45 newtons when placed in an electric field. What is the electric field intensity at this point? Fe = 45 N -0.45 C E=F/q E = 45 N / -0.45 C = -100 N/C • Rank the points in order from greatest electric field intensity to least. C A - D B D, A, C, B Field strength gets weaker as we get farther away from the charge. • Which electron will experience the greatest acceleration? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - A B C + + + + + + + + + + + + + + All three electrons experience the same electric field intensity – this means that they encounter the same force, and so the same acceleration! • What is the direction of the resultant electric field vector at point A? A + 2.0 C + 2.0 C Toward the top of the screen. A test charge placed at point A will not move left or right because it is equally repulsed by both charges in that direction. However, BOTH charges will push it UPWARD. • An electron passes through the electric field between two parallel plates. In which direction will it be deflected? - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + + + + + + + + + + + + + + The electron will deflect toward the positive plate.