* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 332 Unit 7 Momentum student handout
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
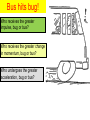
Momentum Momentum is a vector quantity since velocity is a vector. Impulse Defined as a force exerted during a time period Impulse is the cause of a change in momentum. Elastic Cord vs a Steel Wire for same block on frictionless surface Elastic Both the elastic cord & steel wire are equal in length relaxed. The blocks are given a quick, equal push, sending them sliding towards the right. Steel Jumping from table, mats, packaging Compare the impulse provided by both cord & wire from the time they reach their relaxed length to when the blocks stop. Example During an automobile crash test, a 1000kg car is sent towards a cement wall at a speed of 14m/s and is brought to a stop in 0.08 seconds. Determine force car exerted on the wall. Example2 A ball of mass 0.25kg is dropped from a height of 0.75m. The ball bounces back upwards from the floor with a speed of 1.5m/s. a) Determine the speed the ball strikes the floor prior to bouncing back upwards. b) Determine the impulse the ball receives from the floor. Bus hits bug! Who receives the greater impulse, bug or bus? Who receives the greater change in momentum, bug or bus? Who undergoes the greater acceleration, bug or bus? Force-time graph A varying, onedimensional force acts on a 50kg mass as shown in the graph. a) Find the magnitude of the impulse delivered to the object. b) Determine the change in the object's momentum. c) If the object's original velocity was -10m/s, calculate its final velocity. d) What was the magnitude of the "average force" acting on the object during the time graphed? Stick vs Bounce + demo Law of Conservation of Momentum Total momentum before collision equals total momentum after collision assuming no external forces acting during collision. 3 types of collisions • ELASTIC • INELASTIC • Perfectly Inelastic ‘p’ conservation equations KE for collisions Example • Running at 2.0m/s, a 45-kg quarterback, collides with a 90-kg tackle, who is traveling towards him at 7.0m/s. Upon colliding, the tackle continues to travel forward towards the quaterback at 1.0 m/s. Find velocity of quarterback. Example During target practice, a man shoots a 7-gram bullet with a horizontal velocity of 150 m/s directly at a 2-kg pumpkin sitting on a post. If the bullet embeds in the pumpkin, how fast will the pumpkin be knocked off the post? Example An 88kg fullback moving east with a speed of 5.0m/s is tackled by a 97kg opponent running west at 3.0m/s. Assume the collision is inelastic. a) Find the velocity of the two immediately after the collision. b) Find the % of kinetic energy lost during the collision. Example • Jack and Leon are fishing in their boat when they decide to jump into the water. Jack, 45-kg, jumps off the front of the boat with a speed of 2m/s. While at the exact same moment, Leon, 90-kg, jumps out of the back of the boat at a speed of 4m/s. If the boat has a mass of 100 kg and was at rest prior to the two boys jumping off, what will be its velocity just after both boys have abandoned ship? Jumping upwards What happens to the earth, technically speaking, when you jump upwards with glee cuz you can’t wait for physics class? Why? The recoil momentum of a gun that kicks is ____ the momentum of the bullet it fires.