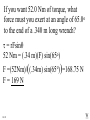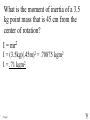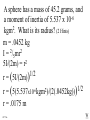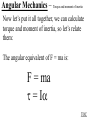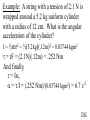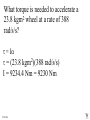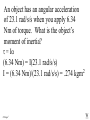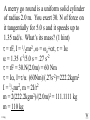* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2AngDyn - TuHS Physics
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Statistical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Automatic transmission wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (mechanics) wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Mitsubishi AWC wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Torque wrench wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Moment of inertia wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
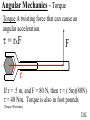
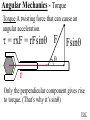
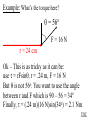
Angular Mechanics - Torque and moment of inertia Contents: •Review •Linear and angular Qtys •Tangential Relationships •Angular Kinematics •Torque •Example | Whiteboard •Moment of Inertia D D •Example | Whiteboard •Torque and Moment of inertia •Example | Whiteboard Angular Mechanics - Angular Quantities Linear: Angular: (m) s - Angle (Radians) (m/s) u o - Initial angular velocity (Rad/s) (m/s) v - Final angular velocity (Rad/s) (m/s/s) a - Angular acceleration (Rad/s/s) (s) t t - Uh, time (s) (N) F - Torque (kg) m I - Moment of inertia TOC Angular Mechanics - Tangential Relationships Linear: Tangential: (at the edge of the wheel) (m) s = r - Displacement (m/s) v = r - Velocity (m/s/s) a = r - Acceleration* *Not in data packet TOC Angular Mechanics - Angular kinematics Linear: s/t = v v/t = a u + at = v ut + 1/2at2 = s u2 + 2as = v2 (u + v)t/2 = s ma = F Angular: = /t = /t* = o + t = ot + 1/2t2 2 = o2 + 2 = (o + )t/2* = I *Not in data packet TOC Angular Mechanics - Torque Torque A twisting force that can cause an angular acceleration. So how do you increase torque? Push farther out: Push with more force: F or F TOC Angular Mechanics - Torque Torque A twisting force that can cause an angular acceleration. = rxF F r If r = .5 m, and F = 80 N, then = (.5m)(80N) = 40 Nm. Torque is also in foot pounds (Torque Wrenches) TOC Angular Mechanics - Torque Torque A twisting force that can cause an angular acceleration. = rxF = rFsin F Fsin r Only the perpendicular component gives rise to torque. (That’s why it’s sin) TOC Example: What’s the torque here? = 56o F = 16 N r = 24 cm Ok – This is as tricky as it can be: use = rFsin, r = .24 m, F = 16 N But is not 56o. You want to use the angle between r and F which is 90 – 56 = 34o Finally, = (.24 m)(16 N)sin(34o) = 2.1 Nm TOC Whiteboards: Torque 1|2|3 TOC What is the torque when you have 25 N of force perpendicular 75 cm from the center of rotation? = rFsin = (.75 m)(25 N)sin(90o) = 18.75 Nm = 19 Nm 19 Nm W If you want 52.0 Nm of torque, what force must you exert at an angle of 65.0o to the end of a .340 m long wrench? = rFsin 52 Nm = (.34 m)(F) sin(65o) F =(52Nm)/((.34m) sin(65o))=168.75 N F = 169 N 169 N W The axle nut of a Volkswagen requires 200. foot pounds to loosen. How far out (in feet) do you stand on the horizontal wrench if you weigh 145 lbs? = rFsin 200. ft lbs = (r)(145 lbs) sin(90o) r = (200. ft lbs)/(145 lbs) = 1.3793 feet r = 1.38 feet (1’ 41/2”) 1.38 feet W Angular Mechanics – Moment of inertia Moment of Inertia - Inertial resistance to angular acceleration. Question - If the blue masses were identical, would both systems respond identically to the same torque applied at the center? Demo TOC Angular Mechanics – Moment of inertia F = ma - We can’t just use “m” for “I” = I (The position of “m” matters!) r F F = ma rF = mar (Mult. by r) rF = m(r)r (a = r) = (mr2) = I ( = rF) So I = mr2 for a point mass, r from the center. TOC Angular Mechanics – Moment of inertia What about a cylinder rotating about its Some parts are central axis? far from the axis Some parts are close to the axis In this case, I = 1/2mr2 (You need calculus to derive it) TOC In general, you look them up in your book. Demos: TP, Solids TOC Three main ones: ½mr2 - Cylinder (solid) mr2 - Hoop (or point mass) 2/ 2 – Sphere (solid) mr 5 TOC Example: Three 40. kg children are sitting 1.2 m from the center of a merry-go-round that is a uniform cylinder with a mass of 240 kg and a radius of 1.5 m. What is its total moment of inertia? The total moment of inertia will just be the total of the parts: Children – use mr2 (assume they are points) MGR – use 1/2mr2 (solid cylinder) I = 3((40kg)(1.2m)2) + ½(240kg )(1.5m)2 I = 442.8 kgm2 = 440 kgm2 TOC Whiteboards: Moment of Inertia 1|2|3 TOC What is the moment of inertia of a 3.5 kg point mass that is 45 cm from the center of rotation? I = mr2 I = (3.5kg)(.45m)2 = .70875 kgm2 I = .71 kgm2 .71 kgm2 W A uniform cylinder has a radius of 1.125 m and a moment of inertia of 572.3 kgm2. What is its mass? I = ½mr2 572.3 kgm2 = ½m(1.125 m)2 m = 2(572.3 kgm2)/(1.125 m)2 m = 904.375 = 904.4 kg 904.4 kg W A sphere has a mass of 45.2 grams, and a moment of inertia of 5.537 x 10-6 kgm2. What is its radius? (2 Hints) m = .0452 kg I = 2/5mr2 5I/(2m) = r2 1/2 r = (5I/(2m)) r = (5(5.537 r = .0175 m .0175 m kgm2)/(2(.0452kg)) x10-6 1/2 ) W Angular Mechanics – Torque and moment of inertia Now let’s put it all together, we can calculate torque and moment of inertia, so let’s relate them: The angular equivalent of F = ma is: F = ma = I TOC Example: A string with a tension of 2.1 N is wrapped around a 5.2 kg uniform cylinder with a radius of 12 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder? I = ½mr2 = ½(5.2kg)(.12m)2 = 0.03744 kgm2 = rF = (2.1N)(.12m) = .252 Nm And finally, = I, = /I = (.252 Nm)/(0.03744 kgm2) = 6.7 s-2 TOC Whiteboards: Torque and Moment of Inertia 1|2|3|4|5 TOC What torque is needed to accelerate a 23.8 kgm2 wheel at a rate of 388 rad/s/s? = I = (23.8 kgm2)(388 rad/s/s) I = 9234.4 Nm = 9230 Nm 9230 Nm W An object has an angular acceleration of 23.1 rad/s/s when you apply 6.34 Nm of torque. What is the object’s moment of inertia? = I (6.34 Nm) = I(23.1 rad/s/s) I = (6.34 Nm)/(23.1 rad/s/s) = .274 kgm2 .274 kgm2 W If a drill exerts 2.5 Nm of torque on a .075 m radius, 1.75 kg grinding disk, what is the resulting angular acceleration? (1 hint) = I, I = ½mr2 I = ½mr2 = ½(1.75 kg)(.075 m)2 = .004922 kgm2 = I, 2.5 Nm = (.004922 kgm2) = /I = (2.5 Nm)/(.004922 kgm2) = 510 s-2 510 s-2 W What torque would accelerate an object with a moment of inertia of 9.3 kgm2 from 2.3 rad/s to 7.8 rad/s in .12 seconds? (1 hint) = I, = o + t 7.8 rad/s = 2.3 rad/s + (.12 s) = (7.8 rad/s - 2.3 rad/s)/(.12 s) = 45.833s-2 = I = (9.3 kgm2)(45.833s-2) = 426.25 Nm = 430 Nm 430 Nm W A merry go round is a uniform solid cylinder of radius 2.0 m. You exert 30. N of force on it tangentially for 5.0 s and it speeds up to 1.35 rad/s. What’s its mass? (1 hint) = rF, I = 1/2mr2 , = o+t, = I = 1.35 s-1/5.0 s = .27 s-2 = rF = 30.N(2.0m) = 60 Nm = I, I=/ (60Nm)/(.27s-2)=222.2kgm2 I = 1/2mr2, m = 2I/r2 m = 2(222.2kgm2)/(2.0m)2 = 111.1111 kg m = 110 kg 110 kg W