* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 8123864
Hamiltonian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Mass in special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
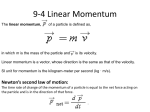
Momentum • All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. • The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables: – how much matter is moving? – how fast the matter is moving? • Momentum: "mass in motion” • Equation: p = m x v • Unit: kg*m/s Momentum • Momentum is a vector quantity. Momentum Consider a Mack truck and a roller skate moving down the street at the same speed. The considerably greater mass of the Mack truck gives it a considerably greater momentum. If the Mack truck were at rest, which would have the greater momentum? If an object is at rest, the momentum of that object is “0” because there is no mass in motion. Momentum Questions 1. Determine the momentum of a ... a.) 60 kg halfback moving eastward at 9 m/s. b.) 1000 kg car moving northward at 20 m/s. c.) 40 kg man moving southward at 2 m/s. Momentum Questions 2. A car possesses 20,000 units of momentum. What would be the car's new momentum if ... a.) its velocity were doubled b.) its mass were doubled c.) both its velocity and mass were doubled If the boulder and the boy have the same momentum, will the boulder crush the boy? Hint: think about the momentum formula! p = mv Impulse • The impulse experienced by an object is the force•time. • The momentum change of an object is the mass•velocity change. • The impulse equals the momentum change. Impulse Force x time = mass x change in velocity F * t = m * Δv Impulse = Change in Momentum N * sec = kg * m/s IMPULSE – A force applied for a period of time which results in a change of momentum. Impulse = change in momentum To change the momentum of a body, a force must be applied to the mass. The longer this force is applied to the mass, the greater effect it will have on changing the momentum. Impulse • A change in momentum in a short time requires a large force. • A change in momentum in a long time requires a small force. 1. An 80 kg skier loses control and demolishes a snow bank. If it takes the skier 3 seconds to come to rest from an impact speed of 9 m/s, find: (a) the impulse on the man (b) the average force exerted on him by the snow bank To change momentum, exert an impulse on it. An outside push or pull is required to change momentum. Hey! It’s the Law! The momentum of a system remains the same unless acted upon by an external force. Can you think of any examples where you think momentum is conserved? Shooting Pool Newton’s Balls Firecracker both sides gain momentum net momenta = zero momentum is conserved Conservation of Momentum What happens to the speed of a fighter aircraft chasing another when it opens fire? What happens to the speed of the pursued aircraft when it returns the fire (from the rear guns)? Bored Astronauts Suppose there are 3 astronauts outside a spaceship. Two of them decide to play catch. All the astronauts weigh the same and are equally strong. The game begins with the first astronaut throwing the second astronaut to the third. How long will the game last? Σ(m1v1) i= Σ(m2v2)f m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f Watch out for negatives!!! Tennis and Cannon Activity • Conservation of Momentumexplosion interaction • pi = pf • m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f Find the velocity of the rifle. -0.75 m/s Follow-up Question: Would you want to fire a rifle that has a bullet ten times as massive as the rifle? Explain. Three Types of Interactions 1. Bouncy Interaction – two objects collide and bounce off each other. No permanent deforming damage. m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f 2. Sticky Interaction – two objects collide and stick together. Final velocities are the same. m1v1i + m2v2i = (m1 + m2)vf 2. Explosion Interaction – two objects explode and move apart from each other. m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f The Next Michelle Kwan…? A softball player wishes to determine her mass. She glides without friction along on some ice skates at 1.5 m/s, and throws a ball of 0.8 kg mass at 27 m/s. She then determines that she has slowed to 1.2 m/s. What is her mass? Ans: m = 68 kg Momentum Railroad Problem of Doom A 500 kg railroad car moving at a speed of 30 m/s collides and sticks together with a 1000 kg railroad car initially at rest. What will be the resulting speed of the cars after the collision? Sample Problem A truck and a car collide head on. The speed of the truck was 20 m/s, and that of the car was 30 m/s. The truck has a mass of 5 times that of the car. If they stick together after the collision, how fast are they moving, as a unit, just after the collision? The Power of Cheese Salami! A 30 g bullet traveling at 300 m/s rips through a 0.65 kg salami and exits at 236 m/s. How fast does the salami move after the bullet leaves? More Momentum If a Mack truck and a Volkswagen have a head-on collision, which vehicle will experience the greatest force of impact? The greatest impulse? The greatest change in momentum? The greatest acceleration? Find the impulse for the following graph. 60 50 40 F (N) 30 20 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 t (s) Conservation of Momentum A golf ball is moving with 1 kgm/s and bounces of a bowling ball initially at rest; after the collision, what is the momentum of the bowling ball? Conservation of Momentum Farmer Joe shoots a bullet of mass 4 g from a gun of mass 7 kg with a speed of 1420 m/s at his collection of coke cans. What is the speed with which the gun recoils? Answer: V = -0.811 m/s Net ∆mv (before collision) = Net ∆mv (after collision) The total momentum before a collision is equal to the total momentum after a collision – Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collision: If the mass of each railroad car is the same, determine the velocity after the collision. m/s m/s 5 m/s You guessed it… MOMENTUM Would a head-on collision between two cars be more damaging to the occupants if the cars stick together or if the cars rebound upon impact? inelastic elastic Sailing, Sailing.. Gilligan’s super escape ice sail craft is stalled on a frozen lake on a windless day. His only piece of auxiliary equipment is a large fan that blows air into the sail. If all the wind produced by the fan strikes and bounces backward from the sail, the craft will move: • • • Backward Forward Not at all Review You jump off a table. When you land on the floor you bend your knees in order to… a.) Decrease the impulse on you by the floor b.) Decrease the force applied to you by the floor c.) Increase the time it takes to stop d.) Both a and b e.) Both b and c f. ) All of the above Review A Mack truck and a Volkswagen have a head-on collision. Which vehicle will experience the greatest force of impact? a.) Mack truck b.) Volkswagon c.) impossible to figure out d.) same Find the impulse for the following graph. 60 50 40 F (N) 30 20 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 t (s)