* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 2 Section 1 - vhhscougars.org
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Sudden unintended acceleration wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
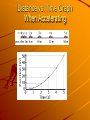
Acceleration Chapter 3 Section 1 What is Acceleration? Speed is the rate of change of position. Galileo defined Acceleration as the rate of change of velocity. – What does that mean it has? HINT Acceleration Hints! Because velocity includes speed and direction of an object, acceleration can be a change in: – How fast the object is moving – What direction the object is moving Acceleration occurs when an object changes its speed or direction, or both! Speeding up or Slowing down? When a car speeds up, that is POSITIVE ACCELERATION! When a car slows down, that is NEGATIVE ACCELERATION or DECELERATION! Acceleration Formula Acceleration = Change in Velocity/Time A = ΔV/T Positive Acceleration A motorcycle starts at rest and accelerates to 80 m/s in 20 seconds A= ΔV/T = 80 m/s/ 20s A= 4 m/s2 Distance vs. Time Graph When Accelerating Negative Acceleration/Deceleration A skateboarder moves in a straight line at 3 m/s and comes to a stop in 2 s. A= ΔV/T =– 3 m/s/2s A= -1.5 m/s2 Free Fall When air resistance doesn’t affect the motion of a falling object, we say the object is in free fall. Downward falling objects gain speed because of the force of gravity. Object thrown Upwards What happens when an object gets thrown upwards? – While going up, it moves against gravity. – At the highest point, when it changes direction from upward to downward, its instantaneous speed is zero. – Then it starts downward just as if it had been dropped from rest. Acceleration Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Acceleration = change in velocity time interval Symbol: A Units: m/s2