Mechanics 1 - Hinchingbrooke
... (b) A girl of mass 48 kg stands in a lift that is going upwards. The lift initially accelerates at 2 ms-2 and then travels at a constant speed of 1.5 ms-1. Finally, the lift decelerates at 3 ms-2. The normal reaction of the floor of the lift on the girl is R N. (i) Draw a diagram showing the weight ...
... (b) A girl of mass 48 kg stands in a lift that is going upwards. The lift initially accelerates at 2 ms-2 and then travels at a constant speed of 1.5 ms-1. Finally, the lift decelerates at 3 ms-2. The normal reaction of the floor of the lift on the girl is R N. (i) Draw a diagram showing the weight ...
OCR GCSE Science Physics A and B PAG 3: Motion
... Learners use a pulley and slotted masses to change the amount of force that causes a trolley to accelerate along a flat surface. They use light gates to work out the acceleration of the trolley with varying forces and plot a graph of their results. Using their graphs learners find the relationship b ...
... Learners use a pulley and slotted masses to change the amount of force that causes a trolley to accelerate along a flat surface. They use light gates to work out the acceleration of the trolley with varying forces and plot a graph of their results. Using their graphs learners find the relationship b ...
Transport Acceleration
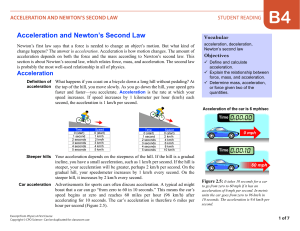
... • If the change in velocity is measured in metres per second (m/s) and the time is measured in seconds, then the acceleration is measured in metres per second per second (m/s2). • For example, if a car accelerates at 2 m/s2,then its speed increases by 2 metres per second every second. • If it was st ...
... • If the change in velocity is measured in metres per second (m/s) and the time is measured in seconds, then the acceleration is measured in metres per second per second (m/s2). • For example, if a car accelerates at 2 m/s2,then its speed increases by 2 metres per second every second. • If it was st ...
Fnet = m a
... motor. So the limiting factor will be friction with the ground. What is the steepest hill (degrees) that a car can drive up at a constant speed of 30 m/sec. if = 0.9 ...
... motor. So the limiting factor will be friction with the ground. What is the steepest hill (degrees) that a car can drive up at a constant speed of 30 m/sec. if = 0.9 ...