* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
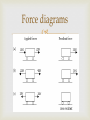
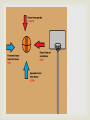
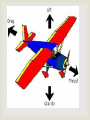
The Laws of Motion Introduction http://www.biography.com/people/isaac-newton9422656 Newton http://www.biography.com/people/galileo9305220 Galileo First Law of Motion An object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force Will this occur forever? What forces act everyday? If forces acting on the object are balanced, then the velocity of the object doesn’t change! Inertia- the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion Examples? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VrWgDnkIjE8&lis t=PL4EE139D689C7CD27&index=1 Second Law of Motion In the presence of a net force, an object experiences an acceleration and it can be calculated as F=ma. It can also be calculated a=F/m Force is measured by Newtons (N), mass is in kilograms (kg), acceleration is m/s2 Remember-acceleration is a vector so it has a magnitude (quantity) and direction! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBSMy8gBGA&list=PL4EE139D689C7CD27&index= 2 Gravity Gravity- is an attractive force between any two objects that depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. The force increases as the mass of either object increases, or as the objects move closer. There are 4 basic forces. They are Electromagnetic-electricity and magnetism, chemical reactions Strong Nuclear Force Weak Nuclear Force Gravity Force diagrams Gravity (continued) The Law of Universal Gravitation- published by Newton in 1687 states that the force of gravity can be calculated between any two objects if their mass and distance between them is known. It states: F= G x m1m2 d2 This is how Neptune’s location was predicted. This is on page 105 in your text book!! G stands for the gravitational constant, which here on Earth is 9.8 m/s2Thanks to Cavendish for this! Moons gravitational constant is around 1.6 m/s2 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-phys-045-gravitational-force Gravitational Acceleration By the 2nd law of motion, the gravitational force exerted by Earth on a falling object is the mass multiplied by the acceleration so: gravitational force (N)=mass(kg) x g (m/s2 ) Free fall-when all forces due to gravity can be ignored, the object is in free fall. The distance covered in free fall can be calculated by: D= at2 2 Weight Weight is the gravitational force exerted on an object. Can be calculated by: Weight (N)=mass (kg) x g g=9.8m/s2 on Earth. What is your weight on the moon? Weight and mass are NOT the same! Weight is a force and mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zSJVCZ2ba0&index=5&list=PL07249EFA9038FDC1 Projectile Motion Draw in notebook! The arrows show the direction of movement! https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/projectilemotion/projectile-motion_en.html Projectile motion Earth’s gravity causes thrown objects to follow a curved path. These horizontal and vertical forces that cause the motion act independently of each other. (honors content) Centripetal Force Centripetal force is the net force toward the center of a curved path Examples? (Gravity can be a centripetal force!) Centripetal acceleration is acceleration toward the center of a curved or circular path. What is velocity doing? Why? Honors content Third Law of Motion When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force on the first that is equal in strength and opposite in direction. Called action reaction pairs or interactive force pairs These forces DO NOT CANCEL EACH OTHER! This is because they are acting on different objects! Example: swimmer in water Interactive Force Pairs Tension Forces Thrust and Drag https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zSJVCZ2ba0&index=5&list=PL07249EFA9038FDC1 Momentum Momentum is a property of a moving object that is related to how much force is needed to change its motion. Calculated by: p=mv The Law of Conservation of Momentum- if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t change Example: playing pool. http://www.bozemanscience.com/momentum Sketch this coaster in your notes. Label all forces and physics concepts on the coaster where they apply! Describe the motion of each line Add scenario to have students create graph