* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Additional Lecture Notes (ppt file)
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Torque wrench wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
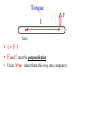
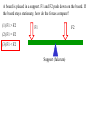
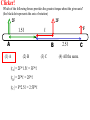
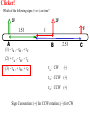
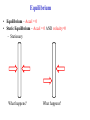
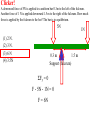
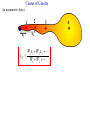
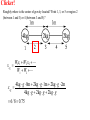
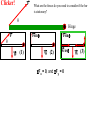
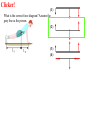
Torque ℓ F Axis • τ = F·ℓ • F and ℓ must be perpendicular. • Units: N*m (enter them this way into computer) A board is placed in a support. F1 and F2 push down on the board. If the board stays stationary, how do the forces compare? (1) F1 > F2 F1 F2 (2) F1 = F2 (3) F1 < F2 Support (fulcrum) Clicker! Which of the following forces provides the greatest torque about the given axis? (the black dot represents the axis of rotation) 2F 2F 1.5ℓ ℓ A F B (1) A (2) B |τA| = 2F*1.5ℓ = 3F*ℓ |τB| = 2F*ℓ = 2F*ℓ |τC| = F*2.5ℓ = 2.5F*ℓ (3) C 2.5ℓ (4) All the same. C Clicker! Which of the following signs (+ or -) are true? 2F 2F 1.5ℓ A (1) - tA , - tB , + tC ℓ F B 2.5ℓ τA : CW (-) (2) + tA , - tB , - tC (3) - tA , + tB , + tC τA : CCW (+) τA : CCW (+) Sign Convention: (+) for CCW rotation; (-) for CW C Levers Small force with long lever arm can exert large force with short level arm Class 1 Lever – Fulcrum between input effort and output load • Pliers • Catapult • Oars • Crowbar • Seesaw Equilibrium • Equilibrium – Accel = 0 • Static Equilibrium – Accel = 0 AND velocity=0 – Stationary What happens? What happens? Example. A uniform board of 10 m is supported at the center. If a person (80 kg mass) is standing 2 m away from the center, how much force is required to balance the board at the other end? F1 F2 Support (fulcrum) Clicker! A force of 5N is applied downward 0.3m to the left of the fulcrum. Where would one exert a force of 1 N downward to balance the the stick? 5N (1) 0.2m to the left (2) 0.2m to the right (3) 1.5 m to the left (4) 1.5 m to the right 0.3 m Support (fulcrum) Στ = 0 (5N)(0.3m) - (1N)L = 0 L = 1.5m Clicker! A downward force of 5N is applied to a uniform bar 0.3m to the left of the fulcrum. Another force of 1 N is applied downward 1.5 m to the right of the fulcrum. How much force is applied by the fulcrum to the bar? The bar is in equilibrium. 5N (1) 2 N. (2) 3 N. (3) 6 N (4) 3.5N 0.3 m 1.5 m Support (fulcrum) ΣFy = 0 F - 5N - 1N = 0 F = 6N 1N Clicker! At which point and at which direction would the least amount of force be required to hold the lever stationary? Longest lever arm - perpendicular force Clicker! Two symmetric objects: a uniform bar and a square box. Where do you draw the weight? A 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) A, C, B, D C, E, F B, E A, C, D, F B C D E F Clicker! An asymmetric object. Where do you think the weight will be centered? 1) 2) 3) 4) A B C D A B C D Center of Gravity (Center of Mass) • • In extended objects, the location where the weight is considered acting on it is the center of gravity. If the object is symmetric, then the "real center“ of the object is the center of gravity. center of gravity • If irregular, one can find the center of gravity using the formula: W1 x1 W2 x2 xcg W1 W2 Center of Gravity An asymmetric object. 1 x1 2 3 x2 W1 x1 W2 x2 xcg W1 W2 4 Clicker! Roughly where is the center of gravity located? Point 1, 3, or 5 or region 2 (between 1 and 3) or 4 (between 3 and 5)? W1 x1 W2 x2 xcg W1 W2 4kg g 0m 2kg g 1m 2kg g 2m xcg 4kg g 2kg g 2kg g 6 / 8 0.75 Clicker! F What are the forces do you need to consider if the bar is stationary? q Hinge q Fsinq F W (1) Fsinq W (2) Fcosq SFx = 0, and SFy = 0 W (3) Torque If the F is not perpendicular to ℓ , then find the F component perpendicular to ℓ . F Fsin q q ℓ Hinge t = (F sin q) . ℓ Note: Check where the angle is given. It could be Fcos q, if the angle is given in other side. Clicker! What is the torque on the fishing pole? Use the end where it is held as the axis of rotation. (1) 80N (cos 20°) 1.2m (2) 80N (sin 20°) 1.2m (3) 80N*1.2m (4) -80N (cos 20°) 1.2m (5) -80N (sin 20°) 1.2m (6) -80N*1.2m Clicker! A cook holds a 2.00kg carton of milk at arm's length. The bicep muscle exerts a force Fb on the forearm. What is the expression for the torque of the bicep muscle on the forearm? Use the elbow as the axis of rotation. (1) (Fbcosθ) 8cm (2) (Fbsinθ) 8cm (3) Fb 8cm (4) -(Fbcosθ) 8cm (5) -(Fbsinθ) 8cm (6) -Fb 8cm (7) None of the above Clicker! The bridge shown must be in static equilibrium. A truck and a car are crossing the bridge. Which of the following force diagrams most correctly describe the forces? (1) (2) (3) (4) Example Write the equation for the net torque. F FT W Fc Clicker! (1) What is the correct force diagram? Assume the gray line as the person. (2) (3) (4)