* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regents Review - Ancient Greece
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Greek mythology wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
First Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
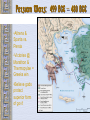
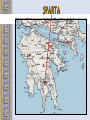
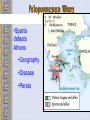
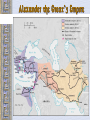
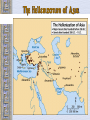
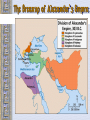
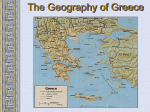
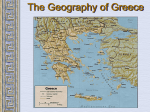
Ancient Greece The Geography of Greece Geography • Peninsula- Mediterranean / Aegean Seas • Sea = trade, ideas • Mountain Valleys divide into city-states • Rocky Islands limit fertile land Agriculture • Good climate but bad terrain (very mountainous) – Hilly ground: grapes – Rocky soil: olives – Good soil: corn and wheat • Sea was very important – Homer describes various fishing methods using hooks, nets, and harpoon in both the Iliad and the Odyssey Bronze Age Greece Crete: Minoan Civilization (Palace at Knossos) Knossos: Minoan Civilization Early Greeks on Crete The Mycenaean Civilization *1st Greek speakers *Seatraders *Influenced by Egypt *Trojan War- economic Rivalry W/ Troy Trojan War • About 1200 B.C., the Mycenaeans fought the Trojan War with the city of Troy in Anatolia • At the same time, foreigners invaded the Mycenaean homeland • From 1100 to 800 B.C., chaos reigned throughout the eastern Mediterranean • In the absence of a centralized state or empire, local institutions took the lead in restoring political order to Greece – City-states The Trojan Horse GREEK GODS • Polytheists- gods live on Mt Olympus • Common Greek culture forms • • • • • • ZEUS = god, humans HERA= marriage POSEIDON = sea APHRODITE = love ARES = war ATHENA = wisdom Homer: The “Heroic Age” *Wandering blind poet *Wrote Iliad and Odyssey “Every man make up his mind to fight and move on his enemy…It’s hard for me to face so many men and with all at once.. And yet I will” - Achilles (the Iliad) Vocabulary –Polis = city-state –Acropolis = High city within polis –Monarchy = King with central power –Aristocracy = Rule by landholding elite –Oligarchy = Small, powerful elite business class rule –Phalanx= formation of heavily armed soldiers ATHENS: Yesterday & Today Most powerful Greek city - state Piraeus: Athens’ Port City Early Athens Monarchy Aristocracy - People begin to resent nobles, wants rights - Democracy = Gov’t by the people Sparta • • • • City-State in south Many captured slaves = strict society Gov’t = 2 kings & council Military society- boys age 7 -30= live in barracks, train • Isolated, frowned on trade, wealth = no new ideas, art, etc… • Becomes rival of Athens- compete for power, influence in Greek world Athenian democracy • Males can vote • 500 man legislature • Slaves, women – no rights • Boys are educated Persian Wars: 499 BCE – 480 BCE •Athens & Sparta vs. Persia •Victories @ Marathon & Thermopylae = Greeks win •Believe gods protect superior form of gov’t Persian Wars: Famous Battles $ Marathon (490 BCE) § 26 miles from Athens $ Thermopylae (480 BCE) § 300 Spartans at the Mountain pass $ Salamis (480 BCE) § Athenian navy victorious Golden “Age of Pericles”: 460 BCE – 429 BCE •Direct Democracy- all males, regardless of wealth / class •Salaries paid to elected officials (poor can serve) •Assembly meets often6,000 + needed to vote •“power is in the hands, not of a minority, but the whole people”- Pericles Great Athenian Philosophers $ Philospher § “Lover of Wisdom” § Believe events not caused by whim of gods § Observe / reason to find real cause $ Examples § Socrates § Plato Aristotle Great Athenian Philosophers $ Socrates § Questions everything § Controversial? § Executed at age 70 for “corrupting youth and disrespecting gods” Great Athenian Philosophers »Plato *Ideal state not democracy - Workers produce - Soldiers defend - Philosophers rule - Wisest = Leader Great Athenian Philosophers • Aristotle –Favors gov’t led by single virtuous leader –Democracy = mob rule Athens: The Arts & Sciences $ DRAMA (tragedians): § Aeschylus § Sophocles § Euripides $ THE SCIENCES: § Pythagoras § Democritus all matter made up of small atoms. § Hippocrates “Father of Medicine” Phidias’ Acropolis The Acropolis Today The Parthenon *Built on the acropolis during the reign of Pericles * Symbol of democracy, classic Greek Architecture Influence of Greek Architecture The Parthenon The Lincoln Memorial The Classical Greek “Ideal” The Ancient Olympics: Athletes & Trainers Great runner, four times victor at the Games, But for a war you would have known no fame. Though exiled from the bubbling springs of home, Your swift pace made a new land's fields your own. - Pindar, Olympian Ode 12, 460BC Olympia: Temple to Hera The 2004 Olympics SPARTA SPARTA Forms Peloponnesian League to counter Athens’ Delian League Peloponnesian Wars •Sparta defeats Athens •Geography •Disease •Persia Macedonia Under Philip II Alexander the Great •Forms vast empire •Cultures blendGreek ideas spread •Alexandria=Egypt. City between 3 continents •Stoicism=philosoph y of life- avoid desires & disappointments by accepting life calmly Alexander the Great’s Empire Alexander the Great in Persia The Hellenization of Asia Pergamum: A Hellenistic City The Economy of the Hellenistic World Hellenistic Philosophers $ Cynics Diogenes § ignore social conventions & avoid luxuries. § citizens of the world. § live a humble, simple life. $ Epicurians Epicurus § avoid pain & seek pleasure. § all excess leads to pain! § politics should be avoided. Hellenistic Philosophers $ Stoics Zeno § nature is the expansion of divine will. § concept of natural law. § get involved in politics, not for personal gain, but to perform virtuous acts for the good of all. § true happiness is found in great achievements. Hellenism: The Arts & Sciences $ Scientists / Mathematicians: § Aristarchus heliocentric theory. § Euclid geometry § Archimedes pulley $ Hellenistic Art: § More realistic; less ideal than Hellenic art. § Showed individual emotions, wrinkles, and age! The Breakup of Alexander’s Empire