* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Greece - Fort Bend ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Eurymedon wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
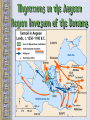
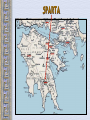
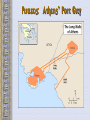
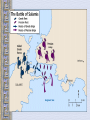
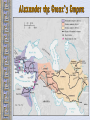
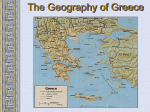
The Geography of Greece Bronze Age Greece Minoan World: 2000-1400 B.C.E. Crete: Minoan Civilization (Palace at Knossos) Aerial View of Knossos Knossos: Minoan Civilization Minoan Civilization Palace of King Minos – North Entrance Palace of King Minos Interiors Palace of King Minos – Throne Room Minoan Ladies Women had rights… Minoan Culture - Religion Minoan Priest Minoan Snake Mother Goddess Religion was based on worshiping the Mother Goddess… Bull Cult …and based on worshiping the Bull. Bull Jumping Fresco Minoan Trade Coast of Crete “Bireme” ship Minoan success was based on trade, not conquest. Minoan Artistic “Motifs” Dolphins represent good fortune and show the importance of the sea. Early Writing System: “Linear A” (Undecipherable) Cannon? What caused the End of the Minoan Civilization?? The Mycenaean World: 1500-1100 BCE View of Mycenae Archaeological “site” Aerial View of Mycenae Mycenae Approach to the Lion’s Gate Lion’s Gate Entrance to Mycenae Mycenaean Writing System: “Linear B” The Mycenaean Civilization The Trojan War What were the real & mythical causes of the Trojan War?? Historically • It is said that Troy controlled trade from the Black Sea to the Mediterranean. • This area was known as the “Vital Straits” Helen of Troy: “The Face That Launched 1000 Ships” What did she look like? Greek Ships Landing on Beaches of Troy Plan of the City of Troy The Nine “Layers” of Ancient Troy Homer’s Troy (VII) Original Wall of the City of Troy Wall of Troy Recreated Dome of King Priam’s Treasury King Priam’s Treasure Mask of Agamemnon Brutal Combat Brutal Combat Troy Grave Circles The “Trojan Horse”? Sir Heinrich Schliemann Homer: The “Heroic Age” Homer, the Blind Poet Homer’s Great Epics Homer’s View of the World Migrations in the Aegean Region Invasion of the Dorians (DORIANS} Greek Culture Declined Greek Culture Declined • Greeks lived in Small Isolated Villages. • Reading and Writing Declined. • Stories were passed on by word of mouth. Early Governments • Monarchy-government in which a king or queen exercises central power. • Aristocracy-rule by a landholding elite. • Oligarchy-power is in the hands of a small, powerful elite, usually a business class. SPARTA: A Nation of Soldiers SPARTA SPARTA Spartans- Dorians that conquered Laconia. Helots – Mycenaean's enslaved by the Spartans. Sparta • Sparta was a Military State. From a young age children (boys) were trained in military tactics. • Women would exercise and keep their bodies in good physical health. • Only men could vote. • Sparta's government had two kings and a council of elders. Sparta’s Military Phalanx- massive formation of heavily armed foot soldiers. ATHENS: A limited Democracy View of the Past Early Athenian Lawgivers $ Corruption in Athens aristocracy had too much power, people called for reform. $ Solon- first to reform the government, made a move for democracy. (594 BCE) $ Pisistratus-further helped the common citizens by offering loans to the poor. (546BCE) $ Cleisthenes- Established the Council of 500 and created the first (limited) democracy. Why was it only a limited Democracy? $ Only male citizens could vote. $ Only male citizens could participate in the government. $ Slavery was still legal. $ Women had no share in life $ Only boys could go to school, if they could afford it. Piraeus: Athens’ Port City Persian Wars: 490 BCE – 479 BCE Persian Wars: Famous Battles $ Marathon (490 BCE) § 26.2 miles from Athens § 25,000 Persians, under Persian Leader Darius‘ § Greeks were out numbered 3 to 1 § Greeks Won Persian Wars: Famous Battles $Thermopylae (480 BCE) § 300 Spartans at the Mountain pass § 25,000+ Persians led by Xerxes § Spartans hold them off till Sparta was betrayed. § Sparta Lost § Persia Marched and burned Athens Persian Wars: Famous Battles $Salamis (480 BCE) § Athenian navy lured the Persian navy into the narrow Strait of Salamis. § Athenian Navy rowed their boats into the Persian Ships and sank them. § Athens is victorious. After the Persian Wars $Greeks felt Strong and realized their place in the world. $Athens emerged as the most powerful City-State. $Delian League was Established – United Greek Allies. Golden “Age of Pericles”: 460 BCE – 429 BCE Direct Democracy was established Golden “Age of Pericles” $Government Thrived $Economy Thrived $Athenian assembly established: 6000 members had to be present $You were paid for government Service. $Judge and Jury $Ostracism – Vote to send away a government official who threatened democracy. Thucydides • Historian who lived in the Age of Pericles. • Recorded events for Athens. Peloponnesian Wars Peloponnesian Wars 431 - 404 BCE (27 years) $Greek vs. Greek $Sparta vs. Athens $Sparta got help from Persia $After the War Athens was no longer a military power. It was however, the center for Greek Culture. Great Athenian Philosophers $ Socrates (469 – 399 BCE) § Know thyself! § question everything § Socratic Method of Teaching § Only the pursuit of goodness brings happiness. § At Age 70 he was put on trial for “corrupting the youth.” § He was sentenced to exile but choose suicide. Great Athenian Philosophers $Plato (Socrates' Student) e The Academy (School) e The Importance of Reason e The Republic (book) His vision of an ideal state. e Did not trust democracy Great Athenian Philosophers $ Aristotle (Plato's’ Student) § The Lyceum (School) Study: Politics, Ethics, Logic, Biology, Literature, Math Etc. § “Golden Mean” [everything in moderation]. § Logic. § Scientific method. Athens: The Arts & Sciences $ DRAMA (tragedians): § Aeschylus § Sophocles (Father of Tragedy) § Euripides $ COMEDY: § Aristophanes (Father of Comedy) Wrote: Lysistrata Athens: The Arts & Sciences $ THE SCIENCES: ۩ Pythagoras Pythagorean Theorem ۩ Democritus all matter made up of small atoms. ۩ Hippocrates – “Father of Medicine” Acropolis The Acropolis Today The Parthenon The Agora Was the term for a Marketplace The Classical Greek “Ideal” Greeks saw the human body as beautiful, they sculpted the body with realism and natural poses but had an idealistic approach. Olympia The Ancient Olympics: Athletes & Trainers Olympia: Temple to Hera The 2004 Olympics Macedonia Under Philip II Macedonia Under Philip II $ Philip conquered and united all of Greece under the Macedonia Empire in 338 BCE. $ Philip was assassinated, Alexander was placed on the Throne. $ In 334 BCE Alexander conquered the weak and often rebellious Persian Empire. (Darius III was Emperor) Alexander the Great Alexander the Great’s Empire Macedonia Under Alexander $ In 331 BCE he took Babylon. $ He conquered Egypt, Persia, India. $ Alexander faced armies that had Elephants and Superior numbers. $ Alexander died of a sudden fever. His Empire was divided up and fought over. The Breakup of Alexander’s Empire Alexander the Great in Persia Hellenistic Culture – assimilation of Greek, Indian, Egyptian and Persian Cultures. The Hellenization of Asia Most lasting achievement was the spread of Greek Culture. The Lighthouse of Alexandria Alexandria Egypt was the center of Hellenistic Culture The Economy of the Hellenistic World Hellenistic Philosophers $ Stoicism - Zeno § nature is the expansion of divine will; just go with the flow § Avoid Desire. § get involved in politics to perform virtuous acts for the good of all. § true happiness is found in great achievements. Hellenism: The Arts & Sciences $ Scientists / Mathematicians: § Aristarchus - heliocentric theory. Idea that sun is center of the solar-system. § Euclid wrote the Element – Modern Geometry § Archimedes – Physics Mastered the idea of a lever and a pulley. $ Hellenistic Art: – More realistic; less ideal than Greek art. – Showed individual emotions, wrinkles, and age !