* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Greece, Persia, and Alexander 546
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Greece wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Ionian Revolt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Prostitution in ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Second Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
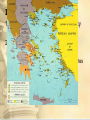
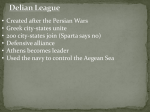
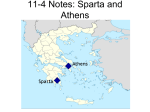
Greece, Persia, and Alexander 546-323 BCE I. Persian Wars 1. Greeks in Ionia (W. Anatolia) rebel; helped by Athens 2. Darius sends large army against Athens • Battle of Marathon 490BCE- greatly outnumbered hoplites humiliate Persians 3. Xerxes sends world’s largest army against Athens 480 BCE 4. Hellenic League 480BCEalliance of Phalanx formation of hoplites city-states led by Sparta defeats Persians 5. Delian League 477BCE- alliance led by Athens drives Persians from Greece • Athena has not been able to soften the lord of Olympus, Though she has often prayed him, and urged him with excellent counsel. Yet once more I address you in words firmer than adamant. When the foe shall have taken whatever the limit of Cecrops Holds within it, and all which divine Cithaeron, shelters, Then far-seeing Zues grants this to the prayers of Athene; Safe shall the wooden wall continue for you and your children. Wait not the tramp of the horse, nor the footmen mightily moving Over the land, but turn your back to the foe, and retire. Yet shall a day arrive when you shall meet him in battle. Holy Salamis, you shall destroy the offspring of women, When men scatter the seed, or when they gather the harvest. (7.141). II. Athenian Power 1. Strongest Greek city-state: naval power 2. Democracy- free, landowning citizens could participate in: a) The Assembly (voting) b) Council of 500- proposed laws c) People’s Courts II. Continued… 1. Philosophers 1. Socrates • • Socratic method- question/answer to find meaning of justice, wisdom, etc. Tried and killed for “corrupting the youth” 2. Plato1. Socrates’ student, started The Academy 3. Aristotle • Started the Lyceum. Wrote about politics, ethics, logic, rhetoric etc.. III. Inequality in Athens 1. Only 15% able to vote – Women, slaves, foreigners had no citizens’ rights 2. 1/3 were slaves 3. Women were confined and oppressed. In Sparta had more freedom 4. Bisexuality among men common IV. Pelopponesian War 431 BCE 1. Athens and Sparta battle for supremacy – Sparta wins with help from Persians 2. Fighting among city-states weakened them – King Philip of Macedonia controls city-states through Confederacy of Corinth V. Alexander the Great (356-323 BCE) • Animated map 1.Conquers Persia, Egypt, Central Asia BY THE TIME HE WAS 30 YRS OLD!! 2.Hellenistic Age • • Establishes Greek-style cities throughout empire Greek culture spread: libraries, universities, science, literature, etc 3.Alexandria- largest, most popular city • In Egypt, housed world’s largest library, museum, research institute Pharos of Alexandria