* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Greece
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
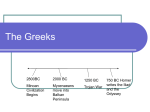
Ancient Greece Beginning of Greece ► Geography pg 1 of Greece had a lot to do with how early Greeks lived. ► Greece has long uneven coastlines ► The sea was very important to the early Greeks, many became sailors, fishers, & traders ► People from Egypt and the Fertile Crescent also came to Greece, bringing goods and ideas along. Geography ► Geography Pg. 2 of Greece kept people from developing a sense of unity. ► Mountain ranges cut up the Greek mainland & kept villages apart. ► Rivers were short & did not aid travel between villages. ► Smaller City-states arose rather than a large united Greece country. Early Greek People ► First Pg. 3 people lived in Greece about 55,000 years ago. ► The Minoan Civilization was the earliest Greek civilization. The Minoan civilization flourished on the island of Crete around 2,000 B.C. ► The Minoan civilization was named after their King Minos who lived in the city of Knossos. ► Minoan people were very advanced, palace and homes were large, running water, toilets, and drainage systems. ► Minotaur- mythical creature that was half bull, half man lived in labyrinth (maze) in Knossos. ►Story of Minotaur and Athenian people. ► Frescoes- paintings made on wet plaster made by artists. ► Maintained Strong Navies ► It was said that a volcano erupted on a nearby island causing tidal waves weakening the Minoan civilization. ► Around 1400 B.C. Mycenaeans from mainland Greece conquered central Crete and the Minoan Civilization. ► Pg. 4 Mycenaean's Pg. 5 ► The Mycenaeans controlled mainland Greece from about 1600-1200 B.C. ► Mycenaeans were a warring people and carried out raids throughout the eastern Mediterranean ► Earthquakes and warfare had destroyed most of the Mycenaean cities by 1200 B.C. ► Mycenaeans adopted many elements of the Minoan civilization after conquering Crete. ►Used Minoan system of writing called Linear B ►Dorian’s sent Greece into Dark Ages with no written records???? City States of Greece ► During Pg 6 the 800’s and 700’s B.C. the Greeks formed a number of individual city-states ► Polis- Greek word city-state ► A polis usually developed around a fort ► Polis came to be known as the fort, its city, and the surrounding farming villages ► Greek people were very loyal to their polis ► Each Polis was absolutely independent and selfsufficient. City-States Cont’d ► Many Pg. 7 of the city-states were alike in many ways. ► They covered a small amount of land and usually had a population of 10,000 people or less. ►Most ► The of these people were slaves or non-citizens. largest two city-states were Athens and Sparta which were about the size of Rhode Island & Connecticut. City States ► Acropolis- Pg. 8 hill or mountain where city-states were built. ► Agora- marketplace, public meeting place. ► Each city-state formed its own government, laws, calendar, money, & system of weights and measures. ► All ancient Greeks had certain things in common; Language (People who didn’t speak Greek were considered Barbarians) Religious Ideas, Culture, Social Patterns & Greek festivals. Greek Government & Society ► Myths – Traditional stories about gods, goddesses, and heroes ► Homer – Blind poet who wrote about Trojan War 500 years after it took place. ► Iliad – Homer’s epic on the Trojan War ► Odyssey – Homer’s epic that tells story of Greek hero Odysseus on way home from Trojan War. ► Olympic Games – Greek Festival including sports, music, and Literature. Pg. 9 ► Oracles – Believed the God spoke through priest & priestesses at these special places. ► Aristocracies – city-states controlled by Nobles ► Hoplite – Greek infantry who carried long spears and fought in closely spaced rows. ► Tyrants – Rulers who seized power by force but who ruled with the people’s support. ► Popular Government – idea that people should rule themselves. ► Democracy – government in which citizens take part. ► Pg. 10 Homeric Age ► During Pg. 11 the Dark Ages, the Dorian people didn’t keep written records. ► During this period few people could write, so most communication was oral, or spoken. ► Since nothing was written, most news was communicated through traveling poets who sang, recited folk songs, ballads, or epics. ► Epic – long poem about heroes and great events. Iliad & Odyssey ► The Pg. 12 Iliad & Odyssey were both written around 700 B.C. by Homer??? ► Homer wrote the Iliad 500 years after it happened. ► The Iliad tells the legend of the Trojan war that talks about the Trojan prince Paris who falls in love with the Mycenaean kings wife Helen. ► Paris kidnaps Helen and takes her with him to Troy. ► The Mycenaeans laid siege to Troy for 10 years but cannot capture the city. ► The Mycenaeans win the battle by building a wooden horse and hiding inside it. ► Meanwhile the Trojans think it’s a “gift” and pull the horse inside the city. Later that night the Mycenaean soldiers leap out of the horse and conquer Troy. ► The Odyssey tells the adventure of the Mycenaean King Odysseus on his way home from the Trojan war which took 10 years. Pg. 13 Greek Religion ► Greeks Pg. 14 looked to Religion for three things. 1) They wanted religion to explain nature ►Ex. They wanted to know what caused lightning, thunder, and the change of seasons. 2) Wanted religion to explain emotions that cause people to lose self control. ►Considered self control very important. 3) Believed religion could bring certain benefits such as a long life, good luck, or a good harvest. ► Did not expect religion to save them from sin. Oracles ► Greeks Pg. 15 gave human qualities and personalities to their gods, who live on Mount Olympus. ► Greeks believed gods spoke through priest and priestesses at special places called the Oracles. ► People often went there to ask questions about the future. Olympics ► Pleasing Pg. 16 Gods was an important part of Greek life and the most important were the Olympic Games. ► Showing strength and bravery in athletic contests were one way to do this. ► The Olympics were held for the first time in 776 B.C. and every four years after that in honor of Zeus. ► Only men could watch and compete and only the winner received wreaths and olive branches. ► There were no second & third prizes. Greek Government Pg. 17 ► Greek city-states that were controlled by nobles were known as Aristocracies. ► Aristocracy use to mean “rule by the best” and over time the term came to describe a privileged social class, usually composed of the wealthiest landowners. ► By the 600’s B.C. wealthy nonaristocrats could afford costly weapons and armor. ► The Hoplite emerged in many parts of Greece. Hoplites were heavy infantry who carried long spears and who fought in closely spaced rows. ► Aristocrats became no match for the powerful hoplite soldiers. ► As hoplites became more important to the defense of the city-state, they demanded more say in its daily government. ► Poor citizens, especially farmers, were unhappy with the rule of the nobles and many began to look for new leaders. Pg. 18 ► Pg. ► The 19 leaders who were able to bring a better life to the people were the Tyrants. ► Early on tyrants ruled well, then slowly they became too powerful and unjust. The word tyrant came to mean someone who uses absolute power brutally. ► Around 650 B.C. many Greek city-states overthrew their tyrants. Government ► In Pg. 20 some of these city-states, the idea of popular government began to take root. ► Some city-states, such as Athens, developed forms of democracy. ► Women and slaves did not have political rights ► Other City-states maintained aristocratic forms of government or restored rule by kings or nobles.