* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Database
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
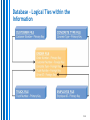
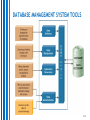
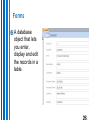
Session 2 Databases • Database Design Principles • Querying and Reporting McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. 2. List and describe the key characteristics of a relational database. Define the common user operations that can be performed within a database management system (DBMS). 3-2 Questions 1. 2. What type of personal transaction information do you maintain? For what purposes? Do you use a computer to help you? What detailed transaction information would a grocery store typically capture and store ? 3-3 INTRODUCTION • • • Businesses use many IT tools to manage and organize information for many reasons Online transaction processing (OLTP) – computer systems used for gathering and processing information and updating existing information to reflect the processed information Online analytical processing (OLAP) – manipulation of information to support decision making 3-4 Information Captured by a Supermarket OLTP INTRODUCTION OLTP Supports operational processing Sales orders, accounts receivable, etc Supported by operational databases & database management systems OLAP Helps build business intelligence Supported by data warehouses 3-6 Operational Databases Source: Database Marketing Institute OLTP, OLAP, and Business Intelligence 3-8 RELATIONAL DATABASE MODEL – collection of information that you organize and access according to the logical structure of the information Relational database – series of logically related two-dimensional tables or files for storing information Database Relation = table = file Most popular database model 3-9 Database Characteristics Collections of information Created with logical structures Include logical ties within the information Include built-in integrity constraints You can’t enter “abcdefg” into a Phone Number field You can’t enter “abcdefg” into a Price field 3-10 Database – Collection of Information 3-11 Database – Created with Logical Structures dictionary – contains the logical structure for the information in a database Data Before you can enter information into a database, you must define the data dictionary for all the tables and their fields. For example, when you create the Truck table, you must specify that it will have three pieces of information and that Date of Purchase is a field in Date format. 3-12 Database – Logical Ties within the Information key – field (or group of fields) that uniquely describes each record Foreign key – primary key of one file that appears in another file Primary Customer Number is the primary key for Customer and appears in Order as a foreign key 3-13 Database – Logical Ties within the Information 3-14 Database – Logical Ties within the Information Customer can place one or more orders. A truck can be used to deliver zero or more orders. An employee can handle one or more orders. A product can be ordered zero or more times. 3-15 Databases – Built-In Integrity Constraints constraints – rules that help ensure the quality of information Data dictionary, for example, defines type of information – numeric, date, text, currency, and so on. Foreign keys – common field found in two or more tables which serves as a primary key in one of those tables. Integrity E.G., a Customer Number in the Order Table (where it is a foreign key) must also be present in the Customer Table (where it is the primary key). 3-16 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM TOOLS management system (DBMS) – helps you specify the logical requirements for a database and access and use the information in a database Data manipulation, data definition, data administration. Database 3-17 Database Management Systems DBMS refers to software used to create, access and manipulate databases. Microsoft Access is a Database Management System. Other examples are: DB2, Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, MYSQL DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM TOOLS 3-19 Objects in a DBMS (e.g. Microsoft Access) Table Query Selecting and viewing records. Form Used for data storage. Data input, display. Report Formatting, calculating, printing, summarizing data. Data manipulation using a DBMS You can add, change, and delete information in a database and query it to find valuable information Users often interact with a database by running queries against it, running reports, or by updating data using forms 3-21 View – allows you to see the contents of a database file, make changes, and query it to find information View Binoculars 3-22 Query A query is a database object that retrieves and processes your data, and then display the results in a datasheet Select query Retrieve only the fields and records you want Filter the records according to your given criteria Sort and group records Perform calculations Retrieve information from a single table or from multiple tables Forms A database object that lets you enter, display and edit the records in a table. Report Generator generator – helps you quickly define formats of reports and what information you want to see in a report Report 3-26 Report Generator 3-27 PRACTICAL SESSION Using Microsoft ACCESS: Explore the structure of a marketing database. Enter new customers and sales orders into a marketing database. Use views, report generators and queries on a marketing database. Adapted from: Haag, Stephen, Cummings, Maeve (2010), Management Information Systems for the Information Age 8th ed, McGraw-Hill International Edition