* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
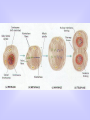
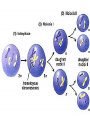
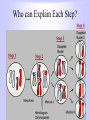
How do we get new cells and new living things? Cell Division Cell Division Meiosis Mitosis • Mitosis, the process • Meiosis occurs during the formation of by which the body gametes in animals. grows and replaces cells, is divided into five phases. Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Mitosis Overview Telophase Interphase Interphase • • • • G1 phase- Cell growth S phase- DNA Replication G2 phase- Preparation for mitosis This is the longest phase of all Prophase • Nucleus Condenses • DNA is compacted into movable packages called Chromosomes Metaphase • Aligning chromosomes at cell equator • Attaching spindle fibers from each new daughter cell pole to each chromosome at the centromere Anaphase • Spindle fibers pull chromosomes apart • Half of the chromosomes (chromatid) moves to a new daughter cell Telophase & Cytokinesis • DNA gathers and two nuclei form • new cell wall and membrane appears between the two nuclei to form two new daughter cells and cytoplasm pinches in half Cell Plate Interphase • From new cell formation into rest phase again Meiosis Gamete Formation and Recombination Meiosis Definition cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; the nucleus divides into four nuclei each containing half the chromosome number leading to gametes. Division 1 • Interphase 1: DNA replication • Prophase 1: Each chromosome forms and remains closely associated. These are called sister chromatids. • Metaphase 1: Homologous chromosomes align at the equatorial plate. • Anaphase 1: Homologous pairs separate with sister chromatids remaining together. • Telophase 1: Two daughter cells are formed with each daughter containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. Division 2 • Prophase 2: DNA does not replicate. • Metaphase 2: Chromosomes align at the equatorial plate. • Anaphase 2: Centromeres divide and sister chromatids migrate separately to each pole. • Telophase 2: Cell division is complete. Four haploid daughter cells are obtained. Web Link to animated Meiosis http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/anisamples/majorsbiolo gy/meiosis.html Who can Explain Each Step? Step 4 Step 3 Step 1 Step 2