* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civilization Begins in Mesopotamia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
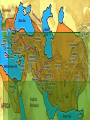
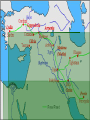
Civilization Begins in Mesopotamia World History The Impact of Geography Mesopotamia: The land between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates The Fertile Crescent: Larger area (from Med. Sea to the Persian Gulf) Impact: Rivers deposited silt when they flooded in late Spring Eventually the people learn to control the water with irrigation and drainage Fertile Crescent Akkadia and Sumeria The Sumerians By 3000 BC there were a number of independent cities in Southern Mesopotamia which developed into citystates The centerpiece of each of these cities was the temple which was built on massive stepped tower called a Ziggurat Government Theocracies: monarchies by divine authority Ziggurat Empires in Mesopotamia Eventually these city states fell into conflict with each other and outside forces 2340 BC The Akkadians and their leader Sargon conquered the region and set up the worlds first Empire (fell in 2100 BC) 1792 BC Hammurabi (leader of the Babylonians gained control of Akad and Sumer Hammurabi’s Code? (eye for an eye) Patriarchal society Religion and Creativity Religion: Polytheistic (3000 or more gods usually associated with nature Creativity: Writing (Cuneiform) to pass down knowledge and record events The Epic of Gilgamesh (immortality for gods only) Technology Bronze (copper and tin), wagon wheel, potters wheel, sundial Assyrians and Persians A Mighty Military Machine 850 BC, the Assyrians advanced from the northern part of Mesopotamia Open area, Little protection Relied on military strength for defense from outside attack Assyrian Empire stretched from north and east of the Tigris river to Egypt Development of Weapons Armor, Weapons, Organization Assyrian Rule 650 BC Height of rule Fell by 612 BC Organization of conquered areas into empire Divided into regions Assyrians choose rulers Taxes and Tribute Assyrian Culture Assyrian Kings were great builders, not just destroyers Nineveh Capital city Ashurbanipal Great warrior Could read many languages Library 25,000 clay tablets Nebuchadnezzar Chaldean King of Babylon (604-562BC) Restoration of Babylon Euphrates through the city Walls 4 Horse Chariot could ride on top Hanging gardens of Babylon Made for homesick wife 75 feet above the ground Hydraulic pumps Babylon fell after Nebuchadnezzar's death to the Persian Empire Rise of the Persian Empire (559 BC -330 BC) Cyrus Ruled from 559-530 BC Military genius, but great Administrator Method of governing Kindness to conquered people Religiously tolerant (opposite of the Assyrians) Darius (522-486 BC) Created an effective style of administration Empire reached its greatest extent Return to toleration and Cyrus’ style of rule Provinces and Royal Road Darius was a great warrior, but his genius was governing 20 provinces Darius still ruled with absolute power Royal Road “Interstate 95” Ran across the Persian empire Satraps (gov’s) Kings eyes and ears 1,677 mile long 111 posts (Rest Stations) Tax collectors Messenger 15 miles apart 7 days Increased trade and communication throughout the empire