* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sun
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Energetic neutral atom wikipedia , lookup
Solar observation wikipedia , lookup
Solar phenomena wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
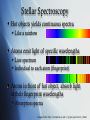
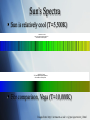
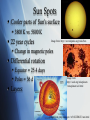
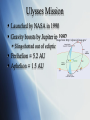
GEOL3045: Planetary Geology Lysa Chizmadia The Sun & Ulysses Introduction Image from: http://seds.org/nineplanets/nineplanets/sol.html Mass = 1.989 x 1030 kg 99.8% of solar system Diameter = 1.39 x 106 km Temperature 5800 (sfc) - 1.56 x 107 K (core) Class G star (G2V) Population I star metallicity high Galactic velocity 2.17 x 105 m/s Galactic period 2.25-2.5 x 108 a Image from: asdictionary.blogspot.com Spectroscopy Pure white light yields continuous spectra, like a rainbow Individual elements produce line spectra like fingerprints Stellar Spectroscopy Hot objects yields continuous spectra Like a rainbow Atoms emit light of specific wavelengths Line spectrum Individual to each atom (fingerprint) Atoms in front of hot object, absorb light at their fingerprint wavelengths Absorption spectra Images from: http://www.arm.ac.uk/~csj/pus/spectra/tot_l.html Sun’s Spectra Sun is relatively cool (T=5,500K) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. For comparison, Vega (T=10,000K) Images from: http://www.arm.ac.uk/~csj/pus/spectra/tot_l.html Sun Spots Cooler parts of Sun’s surface 3800 K vs. 5800 K 22 year cycles Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sun Change in magnetic poles Differential rotation Equator = 25.4 days Poles = 36 d Layers: Image from: http://seds.org/nineplanets /nineplanets/sol.html Image from: nmp.nasa.gov/ st5/SCIENCE/sun.html Aurora Borealis = north Australis = south Images from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aurora_(astronomy) Interaction of solar wind with Earth’s magnetic field Particles have E from 1-100 keV Collisions with oxygen Green and red emissions Collisions with nitrogen Low level red and very high blue/violet Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Aurora_australis_20050911.jpg Ulysses Mission Launched by NASA in 1990 Gravity boosts by Jupiter inImage 1992 from: http://ulysses.jpl.nasa.gov/ Sling-shotted out of ecliptic Perihelion = 5.2 AU Aphelion = 1.5 AU Ulysses (con’t) New solar cycle starting Will be able to study sun spot cycle How does a change in magneticImage from: http://ulysses.jpl.nasa.gov/ field effect solar wind, galactic cosmic rays & us on Earth? Mission highlights: Observed 4 large coronal mass ejections merge into large interplanetary shock wave Feb 2005 Discovered e- jets from Jupiter Feb 2006 Near pass with comet C/2006 P1 McNaught Feb 2007 Summary Sun is main sequence star In mid-life Population I star High metallicity Ulysses mission Launched in 1990 Should reveal how changes in solar magnetic field effect solar wind, background radiation & current technology