* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy - Calendar
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
International Year of Astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
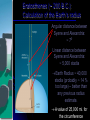
Astronomy In the beginning Pre-test True or False: 1) Greek Astronomers (600BC-150AD) used telescopes to observe stars. Answer: False 2) What lies at the center of our solar system? A) sun B) Mars C) Earth D) the moon Answer: A Pre-test What is a rotation? A) movement around an object B) turning and spinning of a body on it’s axis C) The wobble of a body on it’s axis D) WTBW…these are all correct Answer: B Pre-test What is the approx. rotational period of the Earth? A) 24hrs B) 12hrs C) 30days D) 365days Answer: A Approx. how long does it take for the moon to go through all of it’s phases? A) 24hrs B) 12hrs C) 30days D) 365days Answer: C WTBW How old is the Universe? How many stars are in the Universe? What ancient civilizations contributed to astronomy? Introduction Western astronomy divides into 4 periods Prehistoric (before 500 B.C.) Cyclical motions of Sun, Moon and stars observed Keeping time and determining directions develops Classical (500 B.C. to A.D. 1400) Measurements of the heavens Geometry and models to explain motions Renaissance (1400 to 1650) Accumulation of data lead to better models Technology (the telescope) enters picture Modern (1650 to present) Physical laws and mathematical techniques Technological advances accelerate History of Astronomy 6 Prehistoric Astronomy In summary, basis of prehistoric astronomy: Rising and setting of Sun, Moon, and stars Constellations Annual motion of Sun Motion of planets through zodiac Phases of the Moon Eclipses History of Astronomy 7 The Roots of Astronomy • Already in the stone (4500-2000BC) and bronze ages (3600-1700BC), human cultures realized the cyclic nature of motions in the sky. • Evident in hieroglyphics and cuneiforms • Monuments dating back to ~ 3000 B.C. show alignments with astronomical significance. • Those monuments were probably used as calendars or even to predict eclipses. Great Pyramids ~2589-2504BC Stonehenge Summer solstice Heelstone • Alignments with locations of sunset, sunrise, moonset and moonrise at summer and winter solstices • Probably used as calendar. • Constructed: 3000 – 1800 B.C. Other Examples All Over the World Big Horn Medicine Wheel (Wyoming) Other Examples All Over the World (2) Caracol (Maya culture, approx. A.D. 1000) Ancient Greek Astronomers • Unfortunately, there are no written documents about the significance of stone and bronze age monuments. • First preserved written documents about ancient astronomy are from ancient Greek philosophy. • Greeks tried to understand the motions of the sky and describe them in terms of mathematical (not physical!) models. Ancient Greek Astronomers Models were generally wrong because they were based on wrong “first principles”, believed to be “obvious” and not questioned: 1. Geocentric Universe: Earth at the Center of the Universe. 2. “Perfect Heavens”: Motions of all celestial bodies described by motions involving objects of “perfect” shape, i.e., spheres or circles. Early Ideas of the Heavens Ancient Greek Astronomers Through the use of models and observations, they were the first to use a careful and systematic manner to explain the workings of the heavens Limited to naked-eye observations, their idea of using logic and mathematics as tools for investigating nature is still with us today Their investigative methodology is in many ways as important as the discoveries themselves History of Astronomy 17 Eratosthenes (~ 200 B.C.): Calculation of the Earth’s radius Angular distance between Syene and Alexandria: ~ 70 Linear distance between Syene and Alexandria: ~ 5,000 stadia Earth Radius ~ 40,000 stadia (probably ~ 14 % too large) – better than any previous radius estimate. A value of 25,000 mi. for the circumference Early Ideas of the Heavens The Shape of the Earth Pythagoras taught as early as 500 B.C. that the Earth was round, based on the belief that the sphere is the perfect shape used by the gods By 300 B.C., Aristotle presented naked-eye observations for the Earth’s spherical shape: Shape of Earth’s shadow on the Moon during an eclipse A traveler moving south will see stars previously hidden by the southern horizon History of Astronomy 19 Early Ideas of the Heavens Distance and Size of the Sun and Moon The sizes and distances of the Sun and Moon relative to Earth were determined by Aristarchus about 75 years before Eratosthenes measured the Earth’s size These relative sizes were based on the angular size of objects and a simple geometry formula relating the object’s diameter, its angular size, and its distance Aristarchus realizing the Sun was very large proposed the Sun as center of the Solar System, but the lack of parallax argued against such a model Once the actual size of the Earth was determined, the absolute sizes and distances of the Sun and Moon could be determined History of Astronomy 20 Renissance Astronomy… Group Project Presentations Sing it Take a current song or Broadway number change the lyrics to fit your topic Write it Create a literary piece, a series of sonnets or ballad that reflects your topic Paint it Take your topic and create a masterpiece that represents all components of your topic Dance it Interpretive dance that leaves no question about the interaction in your topic. Kid Book Create a children’s book that tells the story of your topic through illustrations and word. Old Reliable/New Reliable) Tri-fold poster/power point. So what is up There…up there, down there, over there? Where are we? How many stars are out there? How many planets are there…really? How can we see black holes? Is there anything else out there? Is there really a “Global Killer” YOU ARE HERE. A sound that was never heard The Big Bang Model is a broadly accepted theory for the origin and evolution of our universe. It postulates that 15 billion years ago, the portion of the universe we can see today was only a few millimeters across Singularity It has since expanded from this hot dense state into the vast and much cooler cosmos we currently inhabit. WTBW What is the name of the widely accepted theory about the start of the universe? What is the name of the point at which everything started? What ancient civilizations contributed to modern astronomy? History of the Big Bang In 1927, the Belgian priest Georges Lemaître was the first to propose that the universe began with the explosion of a primeval atom. His proposal came after observing the red shift in distant nebulas by astronomers to a model of the universe based on relativity. Years later, Edwin Hubble found experimental evidence to help justify Lemaître's theory. He found that distant galaxies in every direction are going away from us with speeds proportional to their distance. History Continued We can see remnants of this hot dense matter as the now very cold cosmic microwave background radiation (with high powered telescopes) which still pervades the universe and is visible to microwave detectors as a uniform glow across the entire sky. Although the Big Bang Theory is widely accepted, it probably will never be proved; consequentially, leaving a number of tough, unanswered questions. General Theory of Relativity The first key idea dates back to 1916 when Einstein developed his General Theory of Relativity which he proposed as a new theory of gravity. His theory generalizes Isaac Newton's original theory of gravity, c. 1680, in that it is supposed to be valid for bodies in motion as well as bodies at rest. Newton's gravity is only valid for bodies at rest or moving very slowly compared to the speed of light (usually not too restrictive an assumption!). Relativity A key concept of General Relativity is that gravity is no longer described by a gravitational "field" but rather it is supposed to be a distortion of space and time itself. Physicist John Wheeler put it well when he said "Matter tells space how to curve, and space tells matter how to move." Originally, the theory was able to account for peculiarities in the orbit of Mercury and the bending of light by the Sun, both unexplained in Isaac Newton's theory of gravity. In recent years, the theory has passed a series of rigorous tests. WTBW Who is responsible for the Theory of Relativity? How is gravity explained in the Theory of Relativity? What did the theory of relativity explain? What is the distance between the Sun and Earth? The Universe The Universe is made up of millions of galaxies. Also out in space is background radiation from all the explosions and nuclear fusion going on within stars and nebulae. The universe has a whole lot of empty space. In fact, there is so much space even between single stars in a galaxy that it is difficult to measure in miles or kilometers. Space Distance Scientists use a distance measurement in space that is expressed as the distance light will travel in the course of a year a light year. Light travels at a speed of about 186,000 miles per second. That means that light can travel 7.5 times around the entire world in just 1 second! In a year's time, light can travel six trillion miles (6,000,000,000,000). It takes over 4 years for the light from the nearest star to reach the Earth (Proxima Centuri)