* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Feb 2 Student Use
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
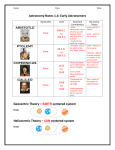
Out of this World Space 13.1 Intro to Space What is Space like? Space is cold, dark, and very empty. Scattered here and there throughout the emptiness are stars, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, meteoroids, and dust. People have spent years looking up at the sky and studying the things in space. First they looked with their eyes, then with telescopes. Today people can travel to space aboard space shuttles, and spacecraft to other planets and moons. What do you know about Space? What do you see when you look up at the night sky? Do you listen to news reports about space missions? Have you ever visited a planetarium? Have you ever noticed that sometimes you can see certain stars more easily than at other times? Or that you can see the stars better if you in one place rather than another? What do you want to know? What other planets are made of? How hot is the Sun? How do astronauts survive in space? Make a list of questions you have about space. How will you find out? You are going to build models and do hands-on explorations that will help you discover answers to many of your questions. Also, the course will include written components, oral presentations, and visual displays. Work will be done individually and in groups, depending on the assignment. Safety Never look directly at the Sun. You can permanently damage your eyes. It only takes a few minutes to do permanent damage! The power of the sun is actually about 4 x 1026 Watts (The Physics Factbook). Scientist Galileo Galilei went blind after observing the Sun with his telescope. Sunspot Loops in Ultraviolet Light – Nearly everything we know and study in Astronomy is based on light, either as a reflection, or an original source Luminous Non-Luminous The Universe The Universe is everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere (EVERYWHERE). By studying stars, planets, and other objects in the sky, you will learn where Earth is located in the universe. You should also understand that we view the universe from a very specific point of view that is unique to Earth (it is a perspective) BLM 13.1a Winter star map: Connect the dots On the hand-out you’ve been given: 1. locate the following constellations as best as you can, 2. then see what other groups you can link together to form recognizable shapes. (use your imagination and be creative) What you just did was basically what early astronomers did hundreds if not thousands of years ago. You are creating a ‘map’ of space based on landmarks and patterns you see. Astronomy Astronomy is the study of what is beyond the Earth. It is the oldest science of all. As early as 2000 BC, Babylonians were using the sundial, the oldest known instrument for telling time. The shadow of the sundial correlates with the Sun’s position in the sky and hence with the time of day. Astronomy vs Astrology Astronomy - The science that deals with the universe beyond our own atmosphere. - Based on observation - Factual Astrology - Not a science, but also deals with things in space - Based on belief and assumptions -Interprets affects of otherworldly bodies on human behaviors Background As an intro into the course, I thought it might be good to lay some groundwork regarding space and the universe http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uihNu9Icaeo& feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KMQk6MveZ OE&feature=related