* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELT Review: 1,2 May 2002 Session 1
Weak gravitational lensing wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
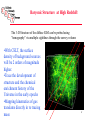
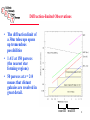
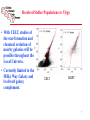
The Science Case Hubble Space Telescope HDF CELT+AO CELT Science Opportunities • New discovery space. – Lesson from Keck is that it is difficult to anticipate the most exciting science areas a decade in advance. Major advances in capability have always resulted in unexpected new discoveries. • Anticipated Science Areas: – – – – – – The development and evolution of structure in the universe The emergence of the first galaxies The physics of star formation The formation and evolution of planetary systems Physical processes in the Solar System The star formation and chemical evolution history of galaxies in the local universe. 2 CELT Science Opportunities • 9x the light gathering capability of a Keck Telescope • 12.5x the spatial resolution of the Hubble Space Telescope with AO • Sensitivity scales between D2 and D4 (factor of 80 improvement!) for different regimes of use (seeinglimited vs diffraction-limited) and source morphology • CELT will be the first facility designed to take advantage of AO and the D4 gain. 3 Baryonic Structure at High Redshift The 3-D Structure of the diffuse IGM can be probed using “tomography” via multiple sightlines through the survey volume •With CELT, the surface density of background sources will be 2 orders of magnitude higher. •Trace the development of structure and the chemical enrichment history of the Universe in the early epochs •Mapping kinematics of gas translates directly in to tracing mass 4 The Birth and Evolution of Galaxies •With 8-10m telescopes we are glimpsing the tip of the iceberg with the first galaxies identified beyond z=1 •Understanding the details of the formation and assembly epoch for galaxies will be a major area in astronomy and astrophysics for the next few decades. The light grasp and spatial resolution of a 30m telescope is essential Spatially dissecting galaxies allows access to physical parameters: mass, chemistry, kinematics (near-IR accesses rest-frame optical for much of the “epoch of galaxy formation”) 5 Diffraction-limited Observations • The diffraction limit of a 30m telescope opens up tremendous possibilities • 1 AU at 150 parsecs (the nearest star forming regions) • 50 parsecs at z = 2-8 means that distant galaxies are resolved in great detail. near-IR mid-IR 6 Resolved Stellar Populations to Virgo • With CELT, studies of the star-formation and chemical evolution of nearby galaxies will be possible throughout the Local Universe. • Currently limited to the Milky Way Galaxy and its dwarf galaxy complement. CELT NGST 7