* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renaissance and Politics “Getting out of the Dark Ages”
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Art in the Protestant Reformation and Counter-Reformation wikipedia , lookup
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
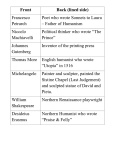
Renaissance & Politics “GettinG out of the Dark aGes” Unit 3, SSWH 9 a & b How did life change during the Renaissance and Reformation? SSWH 9 a & b Explain the social, economic, and political changes that contributed to the rise of Florence and the ideas of Machiavelli. Identify artistic and scientific achievements of Leonardo da Vinci, the “Renaissance man,” and Michelangelo. Renaissance “rebirth” – Revival of art & learning • Europe suffered from both war & plague (Bubonic Plague “Black Death” - 25 million died) • Survivors wanted to celebrate life & the human spirit • People began questioning institutions: church & govt. • Writers & artists began to express this new way of thinking (brought back classic ideas: Greek & Roman) • New value: individual (medieval age: valued the community) p. 410-417 Social & Economic Contributions • Cities in Italy grew, Crusaders traveled through • Pop. Down (plague): worker could demand higher wages • Wealthy merchants (Burghers) developed & got into politics Politics • Merchants dominate politics, believed they deserved power & wealth • Medici Family (bankers) ran Florence as a dictator (with the appearance of a democracy) • Machiavelli, wrote “The Prince” & said people are fickle, selfish, & corrupt • No morals, only concerned with what was effective - “The end justifies the means” Renaissance Man • Educated people, expected to create art • Individuals tried to master all areas of study • Young man should be charming, witty, & well educated in the classics, trained in/as a dancer, singer, poetry, rider, wrestler, & swordsman Humanism p.410-412 • focused on human potential & achievements • Studied Classical texts (Greek & Roman) • Influenced artists and architects Continued • Studied history, literature, and philosophy • Examined traditional teachings of the church Leonardo da Vinci • Painter, sculptor, inventor, & scientist • Interested in how things worked • Famous: paintings Mona Lisa, The Last Supper p.414 Michelangelo Buonarroti • Sculptor, poet, architecture, & painter • Painted realistic portraits, concentrated on the body – used perspective • Famous: painted the dome of St. Peter’s Basilica, Sistine Chapel, & statue of David p. 414 -415 Petrarch •Father of Renaissance humanism •Great poet: wrote both in Italian and Latin Dante • Wrote using vernacular (wrote in everyday local language) and about secular (worldly) things • The Divine Comedy in Italian p. 265 Erasmus “ Christian Humanist” • Christian Humanist • The Praise of Folly • To Improve society, all people should study the Bible Gutenberg & The Printing Press • Chinese invented block & moveable type • 1440, Johann Gutenberg developed a printing press • Process produced books cheaply & quickly p. 418 Continued • First book printed: Gutenberg Bible in 1455 • it increase the amount of available knowledge in society & literacy • Spreading ideas quickly Ticket Out the Door Why is the Renaissance considered a rebirth? Jot answer Prepare to share in one minute