* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renaissance slides
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Early Netherlandish painting wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Art in the Protestant Reformation and Counter-Reformation wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Brancacci Chapel wikipedia , lookup
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
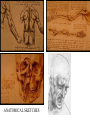
Renaissance Art Painting, Sculpture & Architecture MIDDLE AGES ARCHITECTURE Middle Ages Painting Middle Age Sculpture MIDDLE AGES ART: Cimabue- Madonna •BYZANTINE INFLUENCE •ICONS, RELIGIOUS •NO PERSPECTIVE •NOT REALISTIC •NO INTERACTION WITH OBSERVER •NOT AN ATTEMPT TO DRAW EMOTION •CHILD JESUS: ADULT •LEFT SIDE: DARK •RIGHT SIDE: LIGHT •STRONG SYMBOLISM •MOUNTAINS •EGG- 4 ELEMENTS OF THE UNIVERSE RENAISSANCE ART • EARLY INFLUENCES AND PRECURSORS – CIMABUE • MADONNAS- MORE MIDDLE AGE ART • OLIVE SKINNED DEPICTIONS FOLLOWING MIDDLE AGES TRADITIONS – GIOTTO • • • • SOMETIMES CONSIDERED FIRST RENAISSANCE PAINTER MORE HUMAN, NATURAL PERSPECTIVE IS ACCORDING TO EYE, NOT MATH HUMAN FIGURES HAVE “TACTILE VALUES”- USED LIGHT AND SHAGDE TO 3D EFFECT •GIOTTO: FATHER OF HUMANISM IN PAINTING •Early Renaissance art- beginning to look more natural •Still not a realistic view Madonna Enthroned-Giotto CREATING A NEW ATTITUDE TOWARD ART FROM 1400s- 1500s • PAINTING: MASACCIO • SCULPTURE: DONATELLO • ARCHITECTURE: BRUNELLESCHI MASACCIO •Florentine •Frescoes on the Brancacci Chapel of the Carmine •Early master of human form, emotion •Results of careful observation of human anatomy •Shows skeletal frame and muscle •Use of perspective Peter Baptizing the Neophytes Expulsion from Paradise Use of perspective to depict spatial reality LINEAR PERSPECTIVE •CREATED THROUGH CAREFUL OBSERVATION OF NATURE, INCLUDING ANATOMICAL DISSECTIONS •GOAL WAS TO RECREATE A 3-DIMENSIONAL PHYSICAL REALITY ON A 2-DIMENSIONAL SURFACE. THIS REQUIRED RELATING MATHEMATICS TO ART •THE FIRST TO CARRY OUT A SERIES OF OPTICAL EXPERIMENTS THAT LED TO A MATHEMATICAL PERSPECTIVE WAS THE FLORENTINE ARCHITECT AND ENGINEER FILIPPO BRUNELLESCHI. LORENZO GHIBERTI • “Gates of Paradise” • Old Testament Stories • Ghiberti won a competition for the right to sculpt, create the Bronze doors of the Florence Baptistry • Use of perspective • Defeated Brunelleschi “Gates of Paradise” Doors of St. John the Baptist Ghiberti BRUNELLESCHI WINS IN THE END • Medicis of Florence looking to “redeem themselves spiritually” by giving wealth acquired through banking back to city/church. • Medicis strong sense of civic duty, patronage, and political power- trying to keep popular grasp on Florence’s political scene. • Popes and powerful families looking to become patrons to prove their worthiness and “loyalty to God” • Medicis hired Brunelleschi to complete the long unfinished Cathedral Dome of Florence (he won a contest)- a strong symbol of Medici wealth, power, and success. • Revolutionized architecture “Collonnade of the Annunciation” -use of mathematical perspective -fools the eye RENAISSANCE ARCHITECTURE • RETURNED TO CLASSICAL FORMS: DOMES, CAPITALS, ARCHES, ROMANESQUE • MIDDLE AGES WAS MORE GOTHIC BRAMANTE’S TEMPIETTO Site of crucifixion of St. Peter FURTHERING PERSPECTIVE • SEVERAL ARTISTS BECAME OBSESSED WITH THE NEW TRIUMPHS PERSPECTIVE HAD BROUGHT – PIERO DELLA FRANCESCA – PAOLO UCCELLO – FRA ANGELICO – LORENZO GHIBERTI – LEON BATTISTA ALBERTI Piero della Francesca • Became a master of mathematical perspective • Paintings based on religious teachings coupled with perspective • St. Anthony’s Polyptich in Peruggia • Last 14 years painted nothing and devoted studies to mathematics Vasari claims Uccello loved linear perspective more than his wife! Leon Battista Alberti • Published written work on perspective • Knowledge of perspective spread and became basic aspect of art • Artists began to become consumed by perspective and was the basis of their philosophy Botticelli: Adoration of the Magi BOTTICELLI- TEMPTATION BOTTICELLI- KORAH BOTTICELLI-PRIMAVERA GIOVANNI BELLINI •Master of light •Teacher of Titian, other famous artists •St. Francis in the Desert Bellini’s portrait of the elected rule of Venice, “The Doge” Famous for use of light and attention to detail Venice famous for its portraits Andrea Mantegna •Mantegna represents the transition from Early Renaissance to High Renaissance •North Italy’s greatest Italian artist •St. James Led to His Execution (Destroyed 1944) DONATELLO’S DAVID •15th Century •Considered a founder of the Renaissance •First nude since antiquity •More natural •Counterpoise •Friend and contemporary of Brunelleschiboth journeyed to Romestudying classical relics HIGH RENAISSANCE ARTISTS MICHELANGELO LEONARDO DA VINCI RAPHAEL MICHELANGELO PIETA MOSES MICHELANGELO DAVID MICHELANGELO: SKETCHES/ STUDY OF ANATOMY Use of Counterpoise MICHELANGELO’S SISTINE CHAPEL http://www.historylink101.com/lessons/art_history_lessons/ma/renissance_main_slide.htm LEONARDO DA VINCI THE LAST SUPPER MONA LISA VARIOUS SKETCHES OF DA VINCI SELF PORTRAIT ANATOMICAL SKETCHES LEONARDO DA VINCI VITRUVIAN MAN •PRECISE MEASUREMENTS •MATHEMATICAL RELATIONSHIPS, SPATIAL QUALITY •COMBINES ANATOMY & ARCHITECTURE RAPHAEL SCHOOL OF ATHENS: CLASSICALISM, HUMANISM, PERSPECTIVE MORE RAPHAEL… CHANGE IN ART/ARCHITECTURE MIDDLE AGES • • • • • • • • GOTHIC, CATHEDRALS FLYING BUTTRESSES DARK NO USE OF PERSPECTIVE NO EMOTION NOT REALISTIC NO INDIVIDUAL PORTRAITS STAINED GLASS INSTEAD OF WALL PAINTINGS or FRESCOES • • • • • • • • • ITALIAN RENAISSANCE SYMMETRY/BALANCE USE OF PERSPECTIVE NATURAL LOOKING USE OF CLASSICALISM EMOTIONS 90% RELIGIOUS THEMES FRESCOES INDIVIDUALISM COUNTERPOISE NORTHERN RENAISSANCE • NORTHERN EUROPEAN ART WAS TRADITIONALLY GOTHIC • INFLUENCED BY THE TECHNICAL ADVANCEMENTS OF ITALIAN RENAISSANCE • NORTHERN RENAISSANCE ARTISTS WERE LESS CONCERNED WITH STUDIES OF ANATOMY AND LINEAR PERSPECTIVE • NORTHERN ARTISTS WERE OBSESSED WITH EXQUISITE DETAIL • FAMOUS EARLY ARTISTS OF THE NORTHERN RENAISSANCE: – JAN VAN EYCK – ROBERT CAMPIN – ROGIER VAN DER WEYDEN NORTHERN RENAISSANCE • TOOK GREAT CARE IN • MOST INFLUENTIAL SCHOOL DEPICTING EACH OBJECT OF ART CENTERED IN IN PAINTING- EVEN FLANDERS BACKGROUND • USE OF OIL PAINT ALLOWED • PAINTED ON WOOD- IN VARIETY OF COLORS AND FINE DARK CATHEDRALS DETAILS- OIL WOULD SPREAD TO ITALY JAN VAN EYCK: Giovanni Arnolfini and His Bride, 1434 • SYMBOLISM OF PAINTING AND REFLECTION? – MEMORIAL FOR THE WIFE? – LEGAL DOCUMENT OF A MARRIAGE? Robert Campin Believed to be “Master of Flémalle” Rogier van der Weyden Believed to be the student of Robert Campin Masters of Northern Renaissance • As Italy moved into the High RenaissanceNorthern artists achieved feats equal to those of Italy • These artists included – Albrecht Durer – Hieronymus “Jerome” Bosch – Peter Brueghel – Hans Holbein ALBRECHT DURER MASTER ENGRAVER, PAINTER The Revelation of St John: 4. The Four Riders of the Apocalypse 1497-98 Woodcut Feast of the Rose Garlands, 1506 ALBRECHT DURER: Adoration of the Magi Hieronymous “Jerome” Bosch Garden of Earthly Delights, triptych , 1505-1510 Garden of Eden Centerpiece Hell Peter Brueghel the Elder Children’s Games Hans Holbein, the younger • Famous for realistic portraits, mostly of the court of King Henry VIII Sir Thomas More Henry VIII COMPARING ART OF NORTHERN & ITALIAN RENAISSANCE • • • • ITALIAN NORTHERN • USED FRESCOES, LATER OIL USED OIL ON WOOD • MORE CLASSICAL MORE CHRISTIAN HUMANISM HUMANISM MORE ATTENTION TO • MORE ATTENTION TO LINEAR PERSPECTIVE, FINE DETAIL ANATOMICAL STUDIES USUALLY BRIGHTER TO STAND OUT IN DARK CHURCHES Italian vs. Northern Renaissance Italian Renaissance Northern Renaissance Subject matter: Classical mythology, religious scenes. Domestic interiors, portraits, religious scenes. Style: Symmetrical, balanced, good sense Attention to surface detail, naturalism. of mass, linear perspective. Known for: Figures with mass and volume, knowledge of underlying anatomy. Minute surface detail. Media: Fresco, tempera, oil. Oil on panel. Example: Michelangelo, Creation of Adam from the Sistine Chapel ceiling. Jan van Eyck, Arnolfini Wedding Portrait.