* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The_Digestive_System notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
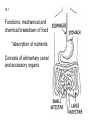
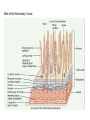
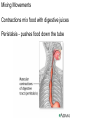
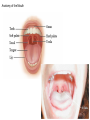
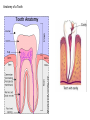
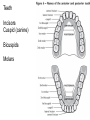
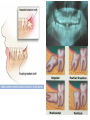
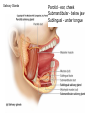
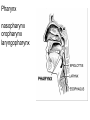
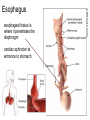
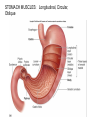
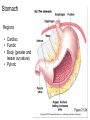
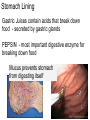
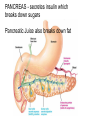
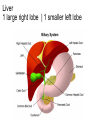
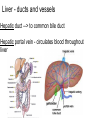
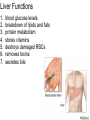
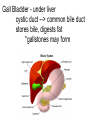
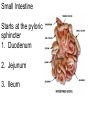
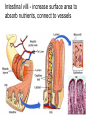
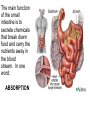
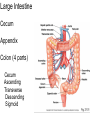
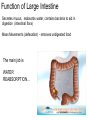
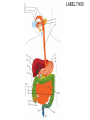
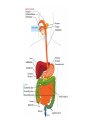
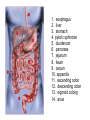
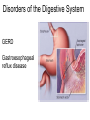
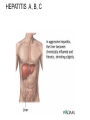
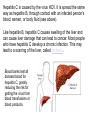
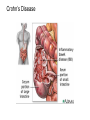
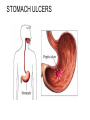
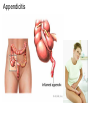
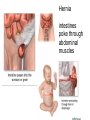
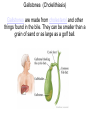
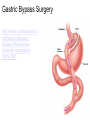
The Digestive System Chapter 15 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics of the Canal 1. Mucosa - protects tissues and carries absorption 2. Submucosa - glands, blood vessels, nerves 3. Muscular Layer - smooth muscle tissue, circular & longitudinal fibers, pushes food (PERISTALSIS) 4. Serosa (serous layer) - visceral perioneum, outer covering of the tube, lubricates surfaces (serous fluid) Mixing Movements Contractions mix food with digestive juices Peristalsis - pushes food down the tube Anatomy of the Mouth Anatomy of a Tooth Teeth Incisors Cuspid (canine) Bicuspids Molars Tooth Decay METH MOUTH ROOT CANAL Salivary Glands Parotid - ear, cheek Submandibular - below jaw Sublingual - under tongue Pharynx nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx Esophagus esophageal hiatus is where it penetrates the diaphragm cardiac sphincter at entrance to stomach STOMACH MUSCLES: Longitudinal, Circular, Oblique Stomach Regions • Cardiac • Fundic • Body (greater and lesser curvature) • Pyloric Stomach Lining Gastric Juices contain acids that break down food - secreted by gastric glands PEPSIN - most important digestive enzyme for breaking down food Mucus prevents stomach from digesting itself Chyme - paste, after food has been broken down, released then into the duodenum via the pyloric sphincter valve Rugae - folds within stomach Gastric Pits contain glands to make juices PANCREAS - secretes insulin which breaks down sugars Pancreatic Juice also breaks down fat Liver 1 large right lobe | 1 smaller left lobe Liver - ducts and vessels Hepatic duct --> to common bile duct Hepatic portal vein - circulates blood throughout liver Liver Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. blood glucose levels breakdown of lipids and fats protein metabolism stores vitamins destroys damaged RBCs removes toxins secretes bile Remember Bili Lights? Using bili lights is a therapeutic procedure performed on newborn or premature infants to reduce elevated levels of bilirubin. If blood levels of bilirubin become too high, the bilirubin begins to dissolve in the body tissues, producing the characteristic yellow eyes and skin of jaundice. Gall Bladder - under liver cystic duct --> common bile duct stores bile, digests fat *gallstones may form Small Intestine Starts at the pyloric sphincter 1. Duodenum 2. Jejunum 3. Ileum Greater Omentum a "curtain-like" membrane that covers the intestines, stores fat and lays like a drape Greater Omentum Intestinal villi - increase surface area to absorb nutrients, connect to vessels The main function of the small intestine is to secrete chemicals that break down food and carry the nutrients away in the blood stream. In one word: ABSORPTION Large Intestine Cecum Appendix Colon (4 parts) Cecum Ascending Transverse Descending Sigmoid Function of Large Intestine Secretes mucus, reabsorbs water, contains bacteria to aid in digestion (intestinal flora) Mass Movements (defecation) - removes undigested food The main job is WATER REABSORPTION... How to Make Fake Poop... LABEL THIS! 1. esophagus 2. liver 3. stomach 4. pyloric sphincter 5. duodenum 6. pancreas 7. jejunum 8. ileum 9. cecum 10. appendix 11. ascending colon 12. descending colon 13. sigmoid colong 14. anus Nutrition Disorders of the Digestive System GERD Gastroesophageal reflux disease Dysentery or Diarrhea HEPATITIS A, B, C Hepatitis A Vaccine Who should get this vaccine? Many people are recommended to receive hepatitis A vaccine, including people at increased risk for exposure to hepatitis A virus infection and people who are more likely to get seriously ill if infected with the virus Hepatitis A is caused by eating food and drinking water infected with a virus called HAV. While it can cause swelling and inflammation in the liver, it doesn't lead to chronic, or life long, disease. Almost everyone who gets hepatitis A has a full recovery, but may need hospitization Hepatitis B is caused by the virus HBV. It is spread by contact with an infected person's blood, semen, or other body fluid. And, it is a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Information on Hepatitis B Some people never develop symptoms, others develop chronic symptoms that stay with them their whole life. Hepatitis C is caused by the virus HCV. It is spread the same way as hepatitis B, through contact with an infected person's blood, semen, or body fluid (see above). Like hepatitis B, hepatitis C causes swelling of the liver and can cause liver damage that can lead to cancer. Most people who have hepatitis C develop a chronic infection. This may lead to a scarring of the liver, called cirrhosis. Blood banks test all donated blood for hepatitis C, greatly reducing the risk for getting the virus from blood transfusions or blood products. Crohn’s Disease IBS - Irritable Bowel Syndrome STOMACH ULCERS Lactose Intolerance Inability to digest milk, can cause stomach upset Appendicitis Hernia intestines poke through abdominal muscles When people with celiac disease eat foods or use products containing gluten, their immune system responds by damaging or destroying villi Without healthy villi, a person becomes malnourished, no matter how much food one eats. Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) Gallstones are made from cholesterol and other things found in the bile. They can be smaller than a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. Gastric Bypass Surgery http://www.hurtbyadoctor.c om/Gastric-BypassSurgery-MalpracticeLawsuits-InformationHome.htm Colon Cancer Colonoscopy is a screening technique to detect cancer. See Katie Couric's Colonoscopy