* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
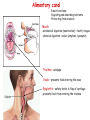
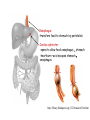
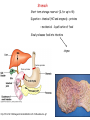
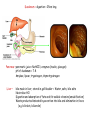
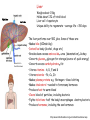
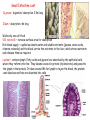
Nutrition photosynthesis Autotroph Herbivores Heterotroph Carnivores Omnivores Nutrition Balanced diet includes all 7 components Energy content of food measured in kilocalories The average teen-ager needs Approximately 2200 calories for girls 2800 calories for boys Carbohydrate- 4.5 calories/g Protein – 4.5 calories/g Fats9 calories/g Obesity New Food Pyramid 2005 - emphasise importance of controlling weight and physical activity - dietary fats – limit saturated fats 20-35% or less of energy should come from fats, healthiest are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated -limit sugar intake -stress benefits of wholegrains Alimentary canal 2 main functions: •Digesting and absorbing nutrients •Protecting from invasion Mouth -mechanical digestion (mastication) = teeth, tongue -chemical digestion = saliva (amylase, lysozyme) Trachea - windpipe Uvula – prevents food entering the nose Epiglottis – safety hatch. A flap of cartilage prevents food from entering the trachea Oesophagus -transfers food to stomach by peristalsis Cardiac sphincter -opens to allow food oesophagus stomach -heartburn –acid escapes stomach oesaphagus http://library.thinkquest.org/11226/main/c03txt.htm Stomach Short term storage reservoir (1L for up to 4h) Digestion = chemical (HCl and enzymes) - proteins = mechanical - liquefication of food Slowly releases food into intestine chyme Cardiac sphincter Pyloric sphincter http://35.9.122.184/images/41-AnimalNutrition/41-16-Duodenum-L.gif Stomach Epithelium Mucous – goblet cells Prevents self-digestion Enzymes (pepsinogen) – chief cells Acid (HCl) – parietal cells Activated to pepsin Converts proteins peptides pH 1-2 Kills bacteria Hormone (gastrin) – G cells Loosens Controlsfibrous gastricfoods motility and Activates pepsinogen acid secretion Denatures salivary amylase Stomach epithelial cells are some of the fastest growing cells in the body, typically replacing themselves about every 3 days Ulcers (stomach, duodenum) – peptic ulcers. Most commonly caused by H. pylori Small Intestine Around 6m in an adult Food takes 1-6 h to pass through 2 main tasks = digestion, absorption 3 parts Duodenum Jejenum Ileum Duodenum = digestion = 25cm long Pancreas –pancreatic juice= NaHCO3, enzymes (insulin, glucagon) pH of duodenum = 7-8 Amylase, lipase, trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen Liver – bile made in liver, stored in gall bladder = Water, salts, bile salts Neutralise HCl Digestion and absorption of fats and fat soluble vitamins (emulsification) Waste products eliminated by secretion into bile and elimination in feces (e.g. bilirubin, biliverdin) Liver Right lobe Left lobe Blood rich in food from ileum Weighs about 1.5kg Holds about 13% of total blood Liver cell = hepatocyte Unique ability to regenerate – average life = 150 days The liver performs over 500 jobs. Some of these are: •Makes bile (600mls/day) •Detoxifies body (alcohol, drugs etc) •Breaks down excess amino acids urea (deamination) kidney •Converts glucose glycogen for storage (source of quick energy) •Converts excess carbohydrates fat •Stores vitamins - A, D, E and K •Stores minerals – Fe, Cu, Zn •Makes plasma proteins e.g. fibrinogen – blood clotting •Makes cholesterol – needed to form many hormones •Produces heat to warm blood •Clears blood of particles, including bacteria •Fights infections –half the body’s macrophages -destroy bacteria •Produces hormones, including the sex hormones http://www.britishlivertrust.org.uk/content/liver/about.asp Small Intestine cont. Jejenum – digestion/ absorption. 2.5m long Ileum – absorption. 4m long Walls only one cell thick Villi, microvilli – increase surface area for absorption Rich blood supply – capillaries absorb water and soluble nutrients (glucose, amino acids, vitamins, minerals) and the blood carries the nutrients to the liver, which stores nutrients and releases them as required Lacteal – contains lymph. Fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed by the epithelial cells where they reform into fats. They become coated in protein (chylomicrons) and pass into the lymph in the lacteals. It takes around 18h for lymph to rejoin the blood, the protein coat dissolves and fats are absorbed into cells Large Intestine 1.5m long, 6cm diameter Food stays 10h to a few days Caecum Appendix Function unknown – in herbivores they contain bacteria that help digest cellulose Colon Reabsorbs water – so waste is converted to semi-solid = faeces – egested Diarrhoea, constipation (fibre helps stimulate peristalsis)