* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 EM Waves Intro
Upconverting nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
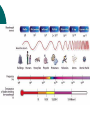
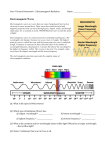
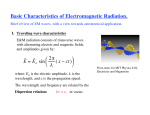
Warm - Up 1. How was Spring Break? What did you do? 2. The School store uses a new pricing system. A vest costs $20, socks: $25, a tie: $15 and a blouse costs $30. Under this system, how much would a pair of underwear cost? Electromagnetic Radiation (EM Waves) Faraday and Ampere’s Laws Electricity and magnetism operate via ‘fields’ Ampere-Maxwell law: A changing Electric field creates a Magnetic field Faraday’s Law: A changing Magnetic field creates an Electric field The created field is perpendicular to the original field. How are EM Waves created Ways to create EM Radiation Moving Charges Why we need antennae Sources of radiation Microwaves Radio Antennae Stars X-Ray Machines Uses? Properties Standard wave properties Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Light Speed The speed of light is a universal constant, It is independent of the frame of reference. 299,792,458 m/s (in a vacuum) Found experimentally confirmed mathmatically 3 * 108 m/s is good enough Written as ‘c’ Electromagnetic spectrum All travel at the same speed but, EM waves are differentiated by wavelength, frequency, energy Flux Rate at which light is emitted from a source (measured in lumens [lm]) Illuminance – illumination of a surface (lm/m2 = lux) Illumination Inverse square relationship Double the distance from a light source, and you decrease by ¼ the illumination Particle nature of light The wave model of light fails when we shine light on zinc, which causes a release of photoelectrons. Increasing the intensity of the light does not always cause more electrons to be released, Emission depends on frequency (color) Photo electric effect Einstein thought light could be quantized Called light quanta: photons Photon energy depends on the frequency of the photon E=h*f h = Planck’s Constant = 6.6 x 10-34 J s F = frequency Work 16.1 – Pg 389 P389 (1-4, 7, 10-12, 16, 20,21, 31-33, 41) Homework Draw an EM spectrum Need to have: Wavelength (units labeled), type of wave, frequency, examples drawn and labeled, also which end is low energy, which is high. See P 374