* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Great Ideas in Science: Lecture 6 – Chemical
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
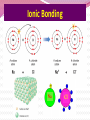
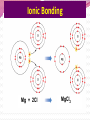
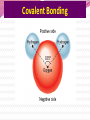
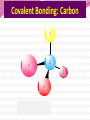
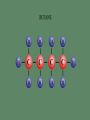
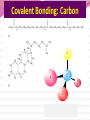
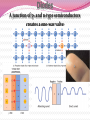
Professor Robert Hazen UNIV 301 KEY IDEA: Properties of materials depend on their atoms, and how those atoms are linked together Tonight’s Outline Review Chemical Bonding Chemical Reactions Properties of Materials States of matter Changes of state Strength of materials Magnetic properties Electrical properties Chemical Bonding Key Idea: Atoms link together by the rearrangement of their electrons 1. “Magic” numbers of electrons (i.e. 2, 10, 18 and 36) form very stable atoms. 2. Electrons may be transferred or shared to form stable bond 3. Ionic, metallic and covalent bonds Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonding Na Cl Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonding Mg + 2Cl Mg + 2Cl MgCl 2 Ionic Bonding Metallic Bonding Metallic Bonding Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonding Hydrogen Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonding WATER Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonding: Carbon 1 C CARBON BONDING Organic2Chemistry 4 3 (R)-enantiomer Covalent Bonding: Carbon 1 CARBON BONDING Organic Chemistry C 4 2 3 (R)-enantiomer States of Matter SOLIDS (fixed volume and shape) Crystal – regular atomic arrangement SOLIDS (fixed volume and shape) Glass: Atoms not periodic Glass vs. Crystal Structure Solids: Plastics Plastics: Formed from chains of molecules Plastic Recycling LIQUIDS (fixed volume, variable shape) LIQUIDS (fixed volume, variable shape) Liquid Crystals: Molecules line up under an electric field GAS (variable volume and shape) PLASMA (Gas with free electrons) By far the most abundant state of matter in the universe!!! Changes of State HYDROCARBONS Distillation (Fractionation) Column Gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, asphalt & tar are distilled from crude oil. Chemical Reactions: Oxidation & Reduction Chemical Reactions: Oxidation & Reduction Rusting = Oxidation Smelting = Reduction Chemical Reactions: Acid & Base Reactions Chemical Reactions: Polymerizaton & Depolymerization Addition Polymerization Chemical Reactions: Polymerizaton & Depolymerization Condensation Polymerization Materials and the Modern World Materials define a society’s technical sophistication Chemists’ contributions Properties of Materials 1) The kind of atoms of which it is made 2) Arrangement of atoms 3) Type of bonding of atoms Different Kinds of Strength Strength Compressive Tensile Shear Elastic Limit Strength depends on the types and arrangements of bonds Compressive Strength: (Strength against squeezing) Stack of paper Masonry Wood Tensile Strength: (Strength against pulling) Wire Rope Chains Shear Strength: (Strength against twisting) Girder network Diamond Composite Materials Combination of materials increases strength Reinforced concrete Plywood Fiberglass Magnetic Properties of Materials Magnetic field Due to electrical current Electrons spinning Arrangement of atomic magnets Degree of alignment determines the strength of magnetism Key Idea Modern electronics control the flow of electrons Metals are conductors of electricity, while ionic and covalently-bonded materials are electrical insulators 2. Semiconductors conduct electricity under carefully controlled conditions 1. Key Words p-type and n-type diode integrated circuit microchip Conductors & Insulators Electrical conductors allow electrons to flow freely. Electrical resistors drain some energy from an electrical current. Electrical insulators prevent the flow of electricity. Semiconductors Semiconductors: neither good conductors nor insulators Example: Silicon Semiconductors: Phosphorus doped n-type Semiconductors Dope with phosphorus One extra electron for each P Semiconductors: Aluminum doped p-type Semiconductors Dope with aluminum A missing electron = hole p-type Semiconductors Dope with aluminum A missing electron = hole Diodes A junction of p- and n-type semiconductors creates a one-way valve The Transistor Transistor Control flow of electrons Emitter Base Collector Uses Cell phone Computer The Transistor as an Amplifier Microchips (Integrated Circuits) Complex array of p- and n- type semiconductors Designed with layers interconnected New materials often lead to new technologies that change society Information The binary digit or bit Two possible answers to a simple question 8 bits = 1 byte All information can be reduced to bits Visual information can be reduced to pixels Two Developing Technologies Computers store and manipulate information Nanotechnology – the future of materials science