* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Judaism - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
The Reform Jewish cantorate during the 19th century wikipedia , lookup
Hamburg Temple disputes wikipedia , lookup
Homosexuality and Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Orthodox Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Interfaith marriage in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on sin wikipedia , lookup
Supersessionism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Origins of Rabbinic Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
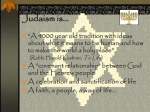
Judaism Judaism One of the three Abrahamic faiths Christianity and Islam 13 million Jewish people in 2007 Most reside in United States and Israel Judaism is the interpretation of the history of the Jewish people “the Jews of the past” Judaism is the sanctification of life- Jews of the present History of Judaism Originated in the Middle East over 3,500 years ago Abraham- Judaism is the Covenant between God and his people Covenant-agreement established a long time ago between God and the ancient Israelites First covenant through Abraham, then through Moses Jews are understood to be God’s Chosen People Exchange for the Covenant, Jewish people keep God’s laws and try to bring holiness to every aspect of their lives History Early history is told in the Hebrew Bible (Old Testament) God chose Abraham, then Moses Became a powerful people with kings like Saul, David and Solomon Judaism’s Central Teachings God’s revelation of the divine will to the Jewish people. Recorded in the Hebrew bible Revelation is called the Torah Judaism’s Central Teachings Master of the Universe: Observant Jews may never pronounce or may avoid pronouncing the divine name Name is written YHWH (Yaweh) Say “Lord” when reading from the Bible One God- only God The Hebrew Bible Three parts: Torah The Prophets The Writings Bible itself is sometimes referred to as the Tanakh Contents are also found in Christian Old Testament But ordered and named differently Torah Literally means ‘instruction’ Refers to the will of God as it is revealed to humankind First five books are thought to have been revealed directly by God to Moses- Jewish laws The Prophets Comprises books that are historical accounts of ancient Israel and proclamations of the will of god spoke to those called to serve God as mouthpieces Prophet means “one who speaks for” The Writings Diverse in both content and literary form Composed later Include: Psalms Proverbs Mishnah & Talmud “oral Torah” is taught by rabbi Teacher of Torah or Jewish worship Mishnah Written down in 200 AD- sacred text Talmud Based directly on Mishnah Grand scheme of interpretation of God’s will The History of the Chosen People Jews were the descendants of the Israelites Exile became known as the Jews Religion known as Judaism (people of Judah) Classical Judaism Earlier Period 587 B.C. Babylonian exile Diaspora 66 A.D. -Jews in Palestine initiated the Jewish War 135 A.D.- Roman rule Medieval Judaism 8th Century- 18th Century Most part lived under the rule of Muslims Generally free to practice their own religion Conditions under Christian rule varied Persecution Sought asylum in Poland Medieval Judaism Moses Maimonides (11351204) Represents a great number of Jewish philosophers Applied philosophy top biblical tradition The Guide for the Perplexed Thirteen Principles Medieval Judaism Kabbalah Jewish mysticism Teaches God can be best known through the heart, through love Does not abandon basic forms of Judaism Modern Judaism Hasidism Meaning ‘pious’ Draws from Kabbalah teachings Emphasizes personal relationships with God and the community, rather than the study of the Torah Modern Judaism Zionism Originally a movement in late nineteenth century Zion- biblical name for Jerusalem Generally refers to the support for Israel Holocaust & AntiSemitism Sometimes called Shoah (Hebrew for mass destruction) Persecution of Jews from 1933-1945 Response Punishment for sins God has broken the Covenant State of Israel Zionist movement- large move of Jews to Palestine 1948- Israel granted statehood Land religious significance for Jews and Muslims Jewish Beliefs & Daily Practices Guided through regulations in the Torah (defines both ethical conduct and worship) Teaches many ethical duties Daily Practices Predominant form of daily worship is through prayer Mandatory only for males over age 13 Women excused for household responsibilities Males required to wear certain accessories Pray at least 3 times daily Home & Synagogue Home Family center Mezuzah Social center the table Synagogue Center of prayer and worship post Babylonian exile Led by rabbis Sabbath Also known as Shabbat Sunset Friday to sunset Saturday Religious and social high point of the week Avoid labor Refrain from usual activities Day of rest, worship and celebration Annual Calendar Holy Days Rosh Hashanah Yom Kippur Passover Rites of Passage Birth and Naming Circumsion Coming of Age Bar mitzvah Bat mitzvah Marriage Death & Mourning