* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acetyl CoA
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
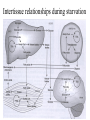
METABOLISM OF ketone bodies Starved state Glycerol-P Glycerol Glucose Triacylglycerol Fatty acyl CoA gluconeogenesis Pyruvate Acetyl CoA TCA cycle Malonyl CoA Ketone bodies Fatty acid Starved state Glycerol-P Glycerol Glucose gluconeogenesis Triacylglycerol Fatty acyl CoA Carnitine transporter Pyruvate Acetyl CoA TCA cycle Malonyl CoA Ketone bodies Glucagon/ epinephrine Fatty acid Ketone bodies • The acetyl-CoA formed in the liver during b-oxidation can have two fates: 1. Enter the TCA cycle 2. Converted to “ketone bodies” – acetone, acetoacetone and b-hydroxybutyrate – for export to other tissues Ketone bodies formed in the liver 1. Condensation of two molecules of acetylCoA, 2. The resulting acetoacetyl-CoA condenses with acetylCoA to form bhydroxy-bmethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) 3. Cleavage of HMG-CoA yields acetyl-CoA and acetoacetate. 4. Reduction of acetoacetate yields D-bhydroxybutyrate (do not confuse with L- bhydroxybutyrate of the boxidation pathway). 5. Acetoacetate is easily decarboxylated (may be spontaneously or enzymatically) to acetone and CO2. Ketone bodies are exported to other organs • Acetone, produced in smaller quantities than the other ketone bodies, is exhaled • Acetoacetate and b-hydroxybutyrate are transported in the blood to tissues other than the liver Ketone bodies as fuels b-hydroxybutyrate may be converted to acetylCoA. The acetyl-CoA is Oxidized in the TCA cycle to provide much of the energy required by tissues Ketone bodies are used under starvation conditions • The brain, which preferentially uses glucose as fuel, can adapt to the use of acetoacetate or b-hydroxybutyrate under starvation conditions, when glucose is unavailable Intertissue relationships during starvation