* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANTILIPEMICS 2012 - students [Read
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
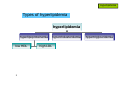
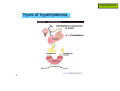
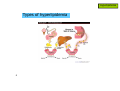
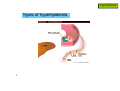
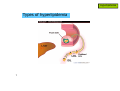
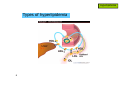
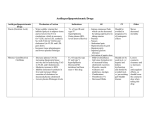
Hyperlipidemia 1 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 2 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia hyperlipidemia hyperlipoproteinemia low HDL 3 high LDL hypercholesterolemia hypertriglyceridemia Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 4 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 5 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 6 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 7 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 8 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 9 Hyperlipidemia Types of hyperlipidemia 10 Hyperlipidemia 2003 11 Hyperlipidemia Background 12 Hyperlipidemia Background 13 Hyperlipidemia Background 14 Hyperlipidemia Background 15 Hyperlipidemia Risk factors • genetic (family history) • lifestyle (obesity, physical inactivity, smoking, atherogenic diet) • emerging markers (homocysteine, proinflammatory factors…) • age (men>45yr, women>55yr) • concomitant diseases: - HTN (>140/90 and/or on anti-HTN Tx) - diabetes - renal-liver disease - hypothyroidism 16 Hyperlipidemia Background NCEP ATP-III classification of LDL, total, and HDL cholesterol LDL cholesterol, mg/dL <100 Optimal 100 to 129 Near or above optimal 130 to 159 Borderline high 160 to 189 High 190 Very high Total cholesterol, mg/dL <200 Desirable 200 to 239 Borderline High 240 High HDL cholesterol, mg/dL 17 <40 Low 60 High Hyperlipidemia Background NCEP ATP-III LDL-cholesterol goals and cutpoints for therapeutic lifestyle changes and drug therapy in different risk categories Risk category LDL level at which to initiate therapeutic lifestyle changes LDL level at which to consider drug therapy coronary heart disease (CHD) or CHD risk equivalent (10-year risk >20%) 100 mg/dL 130 mg/dL; drug optional at 100-129 mg/dL 2 or more risk factors (10-year risk < 20%) 130 mg/dL 160 mg/dL 160 mg/dL 190 mg/dL; LDL-lowering drug optional at 160-189 mg/dL 0 to 1 risk factor 18 Hyperlipidemia 2004 NCEP updates population updated recommendation LDL target of <70mg/dl in very high risk high risk initiate drug therapy at LDL>100mg/dl moderate risk initiate drug therapy at LDL>100mg/dl high/moderate risk intensify drug therapy to reduce LDL by ≥30% NCEP ATP IV expected release – fall 2011 19 Hyperlipidemia 20 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy • HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitors (statins) • fibrates • resins • niacin (vitamin B3) • ezetimibe 21 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy • HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitors (statins) • fibrates • resins • niacin (vitamin B3) • ezetimibe 22 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitors (statins) • simvastatin (Simovil®, Simvacor®, …) • pravastatin (Pravalip®) • fluvastatin (Lescol®) • atorvastatin (Lipitor®) • rosuvastatin (Crestor®) 23 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins 24 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins 25 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins additional mechanism: HMG-CoA reductase inhibition ↓ de-novo cholesterol synthesis depletion of intracellular cholesterol up-regulation of LDL-receptors ↑ internalization of circulating LDL ↓ plasma cholesterol 26 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins T1/2 (hr) atorva fluva prava rosuva simva 14 0.5-2.5 1.5-3 19 2-3 long pharmacological T1/2 allows once daily dosing administer anytime evening evening anytime evening food effect - - ↓ absorption - - metabolites active inactive inactive inactive active solubility lipophilic lipophilic hydrophilic hydrophilic lipophilic % bound 85 99 50 90 95 CYP metabol. + + - +/- + excretion hepatic hepatic 20% renal 10% renal 13% renal LDL reduction 40-55% 15-35% 20-40% 50-65% 30-50% 27 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins PD – LDL reduction Statins also: - ↓ TG - ↑ HDL 28 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins ADEs rhabdomyolysis, myopathy, lactic-acidosis (CK elevations) • rare but potentially life-threatening • risk factors: - statin properties: lipophilicity, dose, DDIs - pre-existing renal function - advanced age - surgery - uncontrolled seizures 29 monitor CK: - baseline - periodically - dose changed <3×ULN: acceptable Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins ADEs rhabdomyolysis, myopathy, lactic-acidosis (CK elevations) N W A R D H WIT 30 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins ADEs • impaired LFTs (monitor, avoid in liver disease) • headaches • sleep disturbances • GI (constipation/nausea/vomiting) 31 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - statins DDIs • mainly affect simvastatin • ↑ levels by itraconazole, amiodarone, diltiazem, verapamil, cyclosporin, fluvoxamine, grapefruit juice • ↑ rhabdomyolysis with other antilipemics • ↑ warfarin levels (all but prava) • ↑ digoxin levels (all but prava, rosuva) 32 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy 33 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy fibrates • bezafibrate (Bezalip®, Norlip®) • ciprofibrate (Lipanor®) 34 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - fibrates PPARα-agonists (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors) 35 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - fibrates bezafibrate / ciprofibrate PK • good oral absorption • non-CYP hepatic metabolism • renal excretion • T1/2 - 2hr / 80hr • IR - TID, SR - double-dose OD / OD 36 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - fibrates ADEs • GI … (mild) • gallstones • ↓ LFTs (?) • headache. dizziness, insomnia • rhabdomyolysis (rare) DDIs - PD, with other anti-lipemics ↓ TG, LDL, ↑ HDL (<statins) 37 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy 38 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy resins (bile-acid sequestrants) • cholestyramine (Chol-Less®, Questran®) • colestipol (Colestid®) 39 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy resins 40 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy resins - PK • oral administration • unabsorbed • not metabolized • “local activity” within GI • fecal excretion 41 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy resins - ADEs • GI – constipation, nausea, flatulence resins - DDIs • impaired intestinal absorption of drugs and nutrients (digoxin, warfarin, aspirin, statins, thiazides, ADEK vitamins, …..) • stagger (1-2hr before, 4-6hr after) mainly ↓ LDL (<statins) 42 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy 43 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy niacin - vitamin B3 (various OTC “nutraceuticals”) high-dose niacin lipolysis in fat tissue ↑ circulating free fatty-acids (FFAs) precursor for triacylglycerol hepatocyte: conversion to VLDL plasma: conversion to LDL 44 HDL increase unexplained Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy niacin - vitamin B3 (various OTC “nutraceuticals”) HDL-raising properties discovered 1955, proposed mechanism published 2008 impaired (-35%) hepatic removal of HDL from blood 45 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy niacin - PK • oral administration • conversion to nicotinamide • incorporated into nicotinamide-adenine nucleotide (NAD+) • renal excretion • fecal excretion 46 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy niacin - ADEs • flushing + warmth (PGD2-mediated cutaneous vasodilation) • SR formulations, “no-flush” derivatives (inositol-hexaniacinate) • USA: a single prescription product (SR, Niaspan®) • prevention: low-dose aspirin 30min prior to niacin? • abdominal pain, nausea, pruritis, liver impairment 47 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy niacin/laropiprant (Tredaptive®) • niacin + peripheral PGD2-receptor selective antagonist • reduced flushing • Approved for use within EU 48 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy niacin - effects • most potent HDL elevation • LDL reduction • TG reduction • may be combined with other antilipemics 49 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy 50 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy • HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitors (statins) • fibrates • resins • niacin (vitamin B3) • ezetimibe 51 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy ezetimibe (Ezetrol®) 52 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy 53 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy 54 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy 55 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy adherence… 56 Hyperlipidemia Pharmacotherapy - hyperlipidemia DRUGS FOR EXAM • simvastatin • bezafibrate • cholestyramine • niacin 57