* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
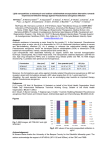
Postantibiotic effect (PAE). In this experiment, fixed inocula of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are exposed to ticarcillin, imipenem, and ciprofloxacin at a set concentration of four times the MIC. The organism and the antibiotic are then diluted 1,000-fold to a point where the antibiotic concentration is far below the MIC of the organism. Growth suppression of S. aureus following exposure to the three drugs (PAE) occurs for approximately 2 hours. Growth suppression of P. aeruginosa, however, is only demonstrated for imipenem and ciprofloxacin. The β-lactam ticarcillin has no effect on the growth of P. aeruginosa. (CFU, colony-forming unit; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration.) (Data from Craig WA, Ebert SC. Killing and regrowth of bacteria in vitro: A review. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl 1991;74:63-70.) Source: Laboratory Tests to Direct Antimicrobial Pharmacotherapy, Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 10e Citation: DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey L. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 10e; 2017 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 13, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved