* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medical Technology Bionics Experiments
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
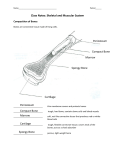
Medical Technology: Bionics Experiments OUTCOME 2: 2.10 gather, identify data sources, plan, choose equipment or resources for, perform a first-hand investigation and analyse information about changes in the heartbeat rate before and after physical activity The heart rate increases when you exercise because your heart and body requires more oxygen and must get rid of carbon dioxide at a faster rate. The heart beats faster and therefore the pulse rate increases. The heart rate of different people will vary due to a variety of factors: - Level of fitness – people with high levels of fitness tend to have faster recovery rate after exercise - Food intake before investigation - Individual differences e.g. body weight Independent variable: amount of activity Dependent variable: rate of the heartbeat Controlled variables: pace of exercise, timing of exercise 2.11 plan and perform an investigation to identify individual aspects that comprise the heartbeat Conclusion—the heart rate changes as the level of physical activity changes. This is because as the pulse rate increases, the body and heart require more oxygen. The cardiovascular system links to the respiratory system to work the body’s muscles. The body and heart needs to get rid of carbon dioxide at a faster rate. The heart contracts in the SYSTOLE phase and relaxed in the DIASTOLE phase. The opening and closing of the heart valves cause “lub dub” sounds. An electrocardiogram records the electrical activity of the heart as it goes through its rhythmic beating process. Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 Electrocardiogram (ECG): TP interval (ventricular diastole): atria and ventricles are relaxed; blood flowing into atria via veins. P wave (atrial systole): SA node fired, atria contracts, forcing all blood into ventricles. QR interval (end of ventricular diastole): the AV valves remain open as all the remaining blood is squeezed into ventricles. RS interval (ventricular systole): as the blood is now all within the ventricles and so pressure is higher here than in atria, the AV valves close. The ventricles start to contract. ST segment (ventricular systole): pressure increase, causing the SL valves to open, blood is ejected into aorta as ventricles contract. T wave (ventricular diastole): ventricles relax; pressure reduced; causing SL valves to close. 2.12 identify data sources, gather, process and analyse information to outline the historical development of pacemakers and use available evidence to identify types of technological advances that 1950 1952 1957 1958 1959 Pacemaker worn externally, had external power source Pacemaker is able to be implanted into patient through surgery Battery-powered pacemaker Internal pacemaker Successful implantable pacemaker Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 have made their development possible 1960s 1970s 1990s Leads that could be fixed to the heart via a vein was introduced Leads with pronged or screw in ends were developed; coating of pacemaker were improved to titanium More sophisticated, much smaller in size, more data can be stored in them 2.13 process information to identify different types of functions of artificial valves in the heart Early pacemakers delivered an electric shock to the heart of the person; device was plugged to wall socket Technological advances that led to the development of the modern day pacemaker: 1. Leads that attach to the wall of the heart 2. Portable battery 3. Surgically implanted 4. Development of smaller pacemakers 5. Improvements in design, battery life, materials used, reprogramming outside the body Mechanical valves E.g. ball and cage metal, disc in cage, bileaflet valve Ball and cage—metal housing with carbon discs; they replicated the function of normal heart valves; very durable Bileaflet valve—two semi-circular discs which open and close; replicate function of normal heart valve; last indefinitely Biological valves E.g. pig, calf, human Made from animal tissue; is treated so it won’t be rejected by recipient; less chances of rejection; degenerate gradually (need replacements) OUTCOME 3: Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 3.11 perform a first-hand investigation to remove calcium compounds from chicken bones to examine the flexible nature of bones 3.12 perform an investigation to examine the relationship between cartilage, muscle, tendon and bone in an animal limb Bones consist of living and non-living parts. The non-living part is made up of calcium which keeps the bones hard & rigid. The living part includes strands of protein, called collagen, which gives bones flexibility. By removing the calcium in a chicken bone, via hydrochloric acid, the hardness of the bone is removed. Calcium & organic matter gives strength to bones. Cartilage is a bluish white rubbery tissue found in humans. It is found at the ends of bones & cushions the bone against shock (shock absorber) which reduces friction. Muscles make the body move. The hold bones of the skeleton together. Muscles move bones by pulling on tendons. A tendon is a strong white cord which connects muscle to bone. When bones meet a joint is formed. Ligaments tie the bones together at the joints (bone to bone). Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 3.13 perform an investigation to demonstrate the different types of joints and the range of movements they allow Types of synovial joints in the body; Body part Shoulder, hip Elbows, knees, ankles Base of thumb Spinal bones, tarsal bones of feet & hands Base of skull (neck) 3.14 process secondary information to compare the shock absorbing abilities of different parts of bones Range of movement of the joint - Side to side - Back & forth - Rotational movements - Back & forth - Back & forth - Side to side - Back & forth - Side to side - End of one bone rotates inside a ring formed by the other bone Type of synovial joint Ball and socket joint Hinge joint Double hinge joint Sliding/gliding joint Pivot joint Comparing bone to cartilage, which has greater shock absorbing ability, why? Cartilage has greater shock absorbing ability than bone because it is flexible. Discuss the shock absorbing ability of the different parts of the bone (e.g. cartilage, tendons, muscle): A bone is generally made up of 2 types of tissue; spongy & compact bone. The spongy, porous part of a bone is less dense & has lower shock absorbing ability. Compact bone is much denser & therefore has a higher rate of shock Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 absorption e.g. arms, legs. 3.15 plan, choose equipment or resources for and perform a first-hand investigation to demonstrate properties of silicone such as acid resistance, flexibility and imperviousness to water that make it suitable for use in bionics 3.16 analyse secondary information to compare the strength of UHMWPE and “superalloy” metal Conclusion – different parts of the bone have different shock absorbing abilities due to their density & structure. The bone has different elasticity than the cartilage between the bones. Cartilage is designed to absorb more shock because it acts as a “cushion” between the bones. It is flexible but strong, supportive tissue. Relating to silicone... Flexibility – very flexible, soft and sticky Resistance to acid – high resistance, does not change shape & hardens slightly to stay together Imperviousness to water – high imperviousness, silicone is not penetrated by water Effect of body temperature – hardens and sticks to itself Independent variable: condition in which the silicone sample is subjected to Dependent variable: flexibility, acid resistance, water imperviousness Controlled variables: time, amount of silicone Silicone has the characteristics of being inert, flexible, water resistant, acid resistant, and easy to shape which makes it an optimal material for the use in bionics. Comparison of stainless steel & titanium alloys; Property Stainless steel Titanium alloy UHMEPE Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene Tensile strength Elasticity Density 960 200 7.8 960 110 4.5 17 700 0.95 OUTCOME 4: 4.6 perform an investigation to model the action of the diaphragm in inhalation and exhalation Air enters the lungs when the chest cavity is expanded. To do this, the ribs are pulled outward & the diaphragm contracts & moves downward. Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 Air is exhaled when the muscles relax & the diaphragm moves up to its original position. 4.7 perform a first-hand investigation to identify carbon dioxide in inhaled air and in exhaled air and determine which has the greater concentration 4.8 gather, process and present information from secondary sources to identify monitoring and other devices that constitute life support systems and use available evidence to explain their roles in maintaining life. Inhalation – diaphragm contracts (moves down) Exhalation – diaphragm relaxes (moves up) The air we breathe in contains about 21% oxygen & 0.03% carbon dioxide. Immediately exhaled air contains 16% oxygen & 4% carbon dioxide. In this experiment, lime water is the indicator of the presence of carbon dioxide. The greater the amount of carbon dioxide the more precipitate is produced & the “whiter” the solution. Kidney dialysis machine The kidney dialysis machine is a device which replaces the function of the kidney when the patient’s kidney is not doing the job adequately. The kidney’s function is to filter blood & remove wastes & toxins from the human body. This dialysis machine filters blood by removing wastes. It is connected to a patient through a tube in the patient’s artery in which the blood flows into the device where the blood is filtered. Then a separate tube carries blood back into a vein into the arm. The kidney dialysis machine as a life support system helps to maintain life by filtering blood which is essential in removing waste from the body. If the wastes were not properly removed Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 then the toxins would build up & the patient can die as a result. OUTCOME 5: 5.4 identify data sources, gather, process, analyse and present information to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of non-invasive and minimally invasive medical techniques Non-invasive techniques General advantages – less risk to patient, fewer side effects, less chance of infections, faster recovery time, less need for medication. General disadvantages – limited number of treatments per year (x-rays have radiation) Advantages & disadvantages of non-invasive techniques; X-rays – Adv; cheap, widely available, provides images of bones & internal organs. Dis; only 2D, may be hard to interpret, cannot see structures deep within tissue, amount of x-rays must be limited (as it can damage or destroy tissue: cancer) CAT scan – Adv; clearer than x-ray, allows the changes in organs as they work to be viewed, e.g. blood flow. Dis; require more skill to interpret images, more expensive Ultrasound – Adv; can examine many areas of the body, pregnancy: no risk to mother or baby. Dis; cannot determine conditions of the bone or lungs. MRI – Adv; provides very detailed images, good for diagnosis of many conditions (MS, tumours, infections, strokes), 3D, no radiation. Dis; some people cannot have MRI (pacemakers, dentures), long procedure, very expensive, difficult for claustrophobic patients. Thermography – Adv; large areas can be assessed, safe & fast, no pain or radiation. Dis; extremely expensive, images are hard to interpret Minimally invasive techniques General advantages – keyhole: allows surgeon to view inside the body without making large incisions, smaller scars, less pain, less risk of infection General disadvantages – endoscopes only allow a small area to be illuminated at a time, may not detect some conditions, risk of infection 5.5 gather, process and analyse information and use available evidence to discuss how How the discovery of ultrasound led to the understanding of blood flow in the body A Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive test that can be used Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014 technological developments have impacted on the understanding of how the body works to estimate the blood flow in blood vessels by bouncing highfrequency soundwaves (ultrasound) off circulating red blood cells. A regular ultrasound uses soundwaves to produce images, but can’t show blood flow. It may help to diagnose many conditions – blood clots, poorly functioning valves in leg veins (venous insufficiency), heart valve defects and congenital heart disease, blocked arteries, decreased blood circulation to legs (peripheral artery disease), bulging arteries (aneurysms), narrowing of arteries. How the discovery of x-rays led to the understanding of bones and its movements The x-ray machine helped to revolutionise how doctors detected disease & injury. X-rays were used in treatment of illnesses like real & imaginary pains. The discovery allowed doctors to see inside the human body for the first time without surgery. X-rays provided insight into our skeletal systems which was an important step in understanding how the human body functions – movement-wise. How antibiotic developments were important in understanding how the body’s immune system works Antibiotics are a group of medicines that are used to treat infections caused by bacteria & certain parasites. Antibiotics do not aid the immune system, it weakens it but replaces one of its functions. They only work on bacterial infections – these chemicals kill the bacteria cells but do not affect cells that make up the body. Sometimes the body’s immune system is unable to activate itself quickly enough to outpace the reproductive rate of harmful bacteria. Other times, the bacteria are producing toxins so quickly they will cause permanent damage before the immune system does it jobs. In these cases, the immune system needs help from something that can kill the invading bacteria directly (antibiotics). Senior Science – By Natalie C 2014