* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download California Geologic History
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
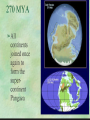
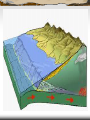
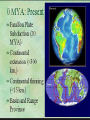
California’s Geologic History Location, location, location… Three continental plates come together Very complex history Introduction Began to form about 2 billion years ago Rock formations that are now adjacent often have very different histories. Some of the larger collisions were associated with major episodes of tectonic activity—intrusive and extrusive volcanic activity, folding and faulting, and mountain building. The most recent period of mountain building is still going on, and practically all of the current landforms and geographic features are very young in geologic terms— only a few million years old. Proterozoic and Paleozoic Era (2,500-245 mya) The oldest rocks, which are more than 1.7 billion years old, are located in the eastern deserts and the San Bernardino and San Gabriel Mountains The distribution of rocks of these ages suggests that the west coast of the North American Continent was well to the east of all but the southern end of what is now California. 1.7 billion year old gneiss After forming from volcanic rock originally, the gneiss was changed by pressure from magma below, intruded into by granite and gabro, then uplifted and eroded. Proterozoic and Paleozoic Era 1,000 million years ago and 400 million years ago appears to have been quiet in western North America. The coastline remained east of California, probably in Utah and Idaho. Very thick sections of marine sedimentary rocks from this period are exposed in the mountains east of the Sierra Nevada. A New Spreading Center Forms Around 700 million years ago a new spreading center formed Rivers that had run into the ocean started to deposit sediment off the coast of North America Eventually reached across the area where California is today End Result of Sediments Sedimentary Rock If over 550 million years old, no fossils Younger rocks do have fossils Evolutionary history is visible Far more in Southern California than Northern Cause: location of sea floor spreading Fossils show CA was underwater Crinoids Trilobites Shells Coral Etc. Mesozoic Era (245-65 million years ago) New growth to California shifted from the spreading center to a convergent plate boundary Uplift of the Nevadan Mountains caused by the formation intrusive granite Volcanic Mountain Ranges formed (Cascades) Surface rocks eroded, creating more sediment to keep building the west coast Metamorphic Rock When rock is affected by heat and pressure, it changes form. Sedimentary coastal rock in the subduction zone became metamorphic rock Later, uplift and erosion re-exposed these metamorphic rocks Paleocene - Eocene 65 to 35 million years ago Mammals show up in the fossil beds now that they are above ocean level Climate was humid, tropical Cenozoic 25-29 million years ago. The spreading center and the subduction zone merged North American and Pacific Plates touched for the first time Western California lifted out of the ocean The San Andreas Fault system was formed. Southern California pulled Northwest East-West stretching of California Tilted fault-block mountains and valleys formed throughout the state Cenozoic (continued) Volcanic Activity formed Mt Lassen & Mt Shasta Pull from the Pacific Plate fragmented California with a number of new faults Some blocks of crust have rotated by more than 90 degrees Fossils indicate drying of the climate, from tropical to arid Today Still Active Geologically San Andreas Fault still active Mountains still growing