* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome_powerpoint_3 - Pearl Public School District
Roman infantry tactics wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Structural history of the Roman military wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
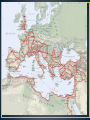
• Rome lies in the center of the Italian Peninsula and Italy is cut off from the rest of Europe by the Alps Mountain Range. • The landscape was far easier to manage than the Greeks, meaning the soldiers were able to march from one end to the other a lot easier than Greeks. • Rome is said to be found by Romulus and Remus. The city of Rome was named after Romulus after he won a deadly battle against his brother. • It was said to be formed around 800 B.C. on top of seven hills near the Tiber River. • They drained the swampy area that kept them apart and built a forum. Forum as the center of government and religion with a little business there too. • First government was a monarchy. The king ruled anything and everything with the help of priests, nobles, and a senate which was made with Wealthy Aristocrats. • Republic- The Romans grew tired of the King and decided to overthrow him and go with a republic which gave people the right to vote. • The word republic comes from the word publica which means public business. • Italy already had many different cultures. People of Rome were diverse. • The early Greeks settled in the area and brought their culture with them. • The Etruscans were highly advanced in Rome and taught the native people everything they needed to know to flourish. • The basic unit of the army was the legion. About 5,000 troops in each army and then broken into maniples. • The army picked up things from other countries such as the sword from Spain and the formation. • They built roads so they could move faster. • Rome’s government was governed by a constitution, or a set of rules by which government if organized. • They focused on a separation of powers, no one man have all the power in the government. • Power was also divided among three branches of government: Assemblies, Senate, and Magistrates. • Free Roman men were citizens of the Roman Republic. Sorry Women. • The symbol for citizenship was the toga, or garment that men wore wrapped around the bodies. • They had the right to a trial when accused and the right to vote. • Two sides: Patricians, older families usually rich, and the Plebeians, normal people who wanted political power. • The assembly was the democratic part of the government. All male citizens could participate in this part with electing officials and passing laws. But they didn’t have as much power as the senate, • The Senate worked like an oligarchy. Made up of the wealthiest and older Roman men. Chosen by the sensor. They were the highest order of the Roman Government and ran the foreign policy and how to spend the money in the city. • Quaestors: dealt with money, Aedile: in charge of festivals and maintain public buildings. Tribune: Protectors of Plebeians. Praetor: Judge Cases, managed the city of Rome, and led the armies. Consuls: top officials of Roman republic, presided of senate and highest judges. • Romans lived in a patriarchal society, meaning that men ruled their families. • The Father had all the power, such as owning property, slaves, and who lived and who died. • Women could own property and take place in society, but couldn’t vote or hold public office. • Rich Romans got there wealth through agriculture and banking and lived in places called villas, or country homes. • Slavery was very big in Rome, in the year 1b.c. there was believed to be 40% of the population were slaves. • Slaves would hold various jobs to mining and farming to working in the house to even teaching school. • They could buy their freedom If they saved up enough money. • The most famous slave was Spartacus who led a major revolt but was put down in the 70’s b.c. • Romans got their religion mostly from other people such as Greeks or the Etruscans. • The government had an established religion, or official religion supported by the government. • The highest officials served as priest and the citizens tried to please them in any way they could. • They built temples, animal sacrifices, held games and build home alters to worship the Gods. • Jupiter: The mighty king of the gods. Roman God of the Sky, thunderstorms, lightning, weather and air. Also god of law, order, justice, governance and strength. Most important god of the Romans and usually had the highest divine authority over other gods. • Neptune: one of the brothers of Jupiter, one of the prime gods and ruler of the seas. The patron of sailors and the protector of ships • Juno: Queen of the Gods and wife of Jupiter. Goddess of Marriage and Women. Protector and Counsellor of Rome. • Mars: God of War, Spring and Justice. Patron of the Roman Legions and divine father of Romulus and Remus. • Venus: Goddess of Love and consort of Mars. Divine mother of Aeneas, ancestor of the Romans. • Bellona: Goddess of War, Conquest and Peace. • Minerva: Goddess of Wisdom, Divine Counsel, Useful Arts and Crafts. Unlike her Greek counterpart, Athena, she wasn't a war goddess. • Janus: God of Beginnings, Endings, Transition, Doorways and Keys. • Vesta: Goddess of the Home and the Hearth. Patron of Rome. • When Romans fought against Carthage for control of the western Mediterranean. • Hannibal, Carthage’s most successful leader attacks and almost destroys the Romans. • Scipio- Roman General that attacks Carthage and defeats Hannibal for the end of the Punic Wars. • Roman troops burn Carthage to the ground and took control of all land in western Mediterranean. • This started the Roman Empire. • Carthage was a city in North Africa that also controlled parts of Spain and Sicily. • Hannibal, Carthage's most successful general, led his city’s troops. • In 218B.C.he launched a daring strike. • Hannibal marched from Spain into Italy over the Alps mountains with 40,000 soldiers and about 40 war elephants. • In 204B.C., the Roman general, Scipo, crossed the sea into Africa, his army then attacked Carthage. • Corrupt Rulers were sent to govern the new lands, kill anybody that sought to get in their way. • Poor Romans were growing with overwhelming numbers. Tenant farmers lost jobs. • Gaius Marius- Great Consul that helped poor Romans to join army and get jobs. • Military Commanders were turning their armies against the senate causing civil war, or war between groups in same country. • Julius Caesar- Powerful Military leader who took over Rome and helped the poor. Died by stabbing from the senate on the day call Ides of March, or March 15, 44 b.c. • Octavian defeated Caesars enemies and created an empire and called himself Augustus, or greatly honored one. • Augustus- Brought peace to Rome after the civil wars. Shrank the size of military, improved life for ordinary people, and fought corruption. • Trajan- New Territory, • Hadrian- Travelled around the empire, • Marcus Aurelius- Famous book of Philosophy. • Nero- Persecuted Christians and killed for no reason. • Pax Romana- Roman Peace from 30 B.C. to 180 A.D. • Roman Roads- one old saying is, “All Roads Lead to Rome” • Roman Roads were built to last. The paved roads extended more than 50,000 miles which lead to cities and forts. • The roads were built mainly so that soldiers could move from place to place. • Many people worked on the roads including military engineers, stonemasons, and surveyors. Roman soldiers also worked on the roads when they were not fighting. • The roads helped make government and trade more efficient. • Good roads from ports to large inland cities also helped supply food. • An aqueduct is a water supply or navigable channel constructed to convey water. • The Roman aqueduct at Pont du Gard, near Nîmes, France, was and still is a very important aqueduct; which was built between the late 1st century B.C. and the early 1st century A.D. • The Roman aqueducts not only provided drinking water for the Romans, but indoor sewer systems that carried water away from the city and also supplied the baths and, other modern day household things, with abundant amounts of water. • Architecture- They made things out of concrete instead of stone which was much lighter. They built domes and arched bridges. • • • • The best preserved building from ancient Rome built between 118 to 125 A.D. in the reign of Hadrian Was a Roman temple dedicated to all the gods of Rome The single round openings called an oculus located at the highest point in the dome • The oculus at the top of the Pantheon is 28 feet in diameter and provides the only source of light for the interior. • • • • built around 70 A.D. It is a multilevel system of vaults made of concrete real name is the Flavian Amphitheater used for staged battles between lions and Christians and gladiators • Rome did a lot of trading by sea which was safe after they made a navy. • The economy was based on farming. This is where people got the money for public buildings. • Crafts were also part of economy such as glass, pottery, metalwork, and ships. • They established one united currency so trading would be easier. • Art- Colorful mosaics brightened the floors, which were designed with small tiles of glass, stone, or pottery. • Roman Languages- Spanish, Italian, French, and Portuguese all originated from Latin which was spoken throughout Europe. • Oratory- Romans created the art of giving speeches, like Cicero who spoke about politics. • Virgil- Wrote and told the story Aeneid, a copy of the Illiad and the Odyssey. Juvenal- Wrote satires which made fun of the Roman Empire. Seneca- Stoic writer who urged people to practice self- control. Claudius Ptolemy- Famous astronomer and mathematician, wrote a book on how to view the universe even though it was wrong, and wrote about Geography and light as well. Claudius Galen- Physician who cut open animals to study the body. • They enjoyed many events such as fights and athletic contest. • Gladiators- Men who fought one another for entertainment usually to the death. Fought in the Coliseum. http://channel.nationalgeographic.com/when-rome- ruled/videos/gladiator-training-camp/ • Sometimes it would teams of Gladiators and then other times there would be water battles so the gladiators could fight naval battles. • Chariot Races- Held in Circus Maximus, Romans would race chariots pulled by horses. • Roman Law- Twelve Tables- Laws about Roman Life but significant because it was written down. http://www.tcm.com/mediaroom/video/224881/Ben-Hur-Movie-Clip-Chariot-Race-Action.html Problems, including civil wars and foreign invasions, led to the decline of the Roman empire. The Roman empire was divided into eastern and western halves, each with its own emperor. The western half of the Roman empire collapsed while the eastern half survived. Military commanders began challenging emperors. A series of civil wars broke out. Septimus Severus tried unsuccessfully to restore peace. More civil wars occurred. Two Important Emperors Diocletian • split the empire into two halves • reorganized the imperial government into two co-emperors with junior emperors for support • restored peace on the frontier • persecuted Christians Constantine • made Christianity a legal religion in the empire • started to build a new capital for the eastern empire, in the city now called Constantinople How did the fall of the Roman empire lead to movement of all sorts?