* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Egyptians
Animal mummy wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
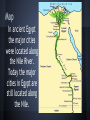
Ancient Egyptians Brianna Courteau, Eva Moynihan, and Josephine Bowen Map In ancient Egypt the major cities were located along the Nile River. Today the major cities in Egypt are still located along the Nile. Time Line Natural Resources Reeds that surround the Nile are used to make mats, sandals, and baskets. The mud the reeds grew in was used to make pottery. Papyrus grew around the Nile and was made into a paper that was easy to write on with ink. Other resources: ● gold ○ new level of sophistication to European society ● natural salts (natron, brine and soda) ○ used in medicine, to flavor and preserve food, tan animal hides, and to mummify ● sandstone and limestone ○ build temples, palaces and tombs ● flax ○ used for oil and fiber Language/Communication The official language of Ancient Egypt was Coptic. Coptic is a variant of the Greek alphabet and was the official language until the Arabs conquered Egypt. Today the official language of Egypt is Arabic. Hieroglyphics “Sacred Carving” “Language of the gods” were used mostly by upper-class because hieroglyphics were time consuming to learn and create. Social Organization King Tut Pharoah- connecter between gods and earth leader of the people ● ● ● ● He ruled the people and was seen as a religious man. King Tutankhamun began his rule at 19 years old and was murdered shortly after. Akhenaten changed the religion. Because many people did not agree, his monuments were destroyed and his name was scratched off of statues shortly after his death. 1479- Hatshepsut began rule after she was widowed by Thutmose II. Social Organization ● ● Women were equal with men before the law. They had the right to file for divorce. Had different social classes that were determined by the occupation starting with the pharaohs on the top and ending with salves on the bottom. Trade and Commerce ● Grain was mainly used as money. ● Internal trade and commerce was done by bartering. ● Egypt lacked horses and trees, so the people of Egypt traded with other areas that had the resources they needed. Infrastructure City-states were mainly located by the Nile Early houses were made of papyrus reeds. Later, the rich could afford to build their houses out of stone but the middle and lower class houses were made of mud bricks and straw. living areas were on the roofs Infrastructure Pyramids: houses for the dead Smooth angled sides = rays of the sun. Easier for pharaoh's soul to ascend to heaven. Built by 20,000 skilled laborers, not salves! The Great Pyramid of Giza, 2600 BC Saqqara, Egypt 2700 BC Religion ● Polytheistsic - believed in many gods ● believed in an afterlife ● believed your heart was weighed on a scale. On the other side of that scale was a feather of truth and justice called the ma’ at ● Ammit was the creature that ate the evil hearts Some of the gods and goddesses ➢ Ra: god of the sun, first pharaoh of the world ➢ Geb: goddess of the sky ➢ Nut: god of the earth ➢ Shu: god of air ➢ Osiris: god of the underworld ➢ Anubis: god of the funerals ➢ Set: god of deserts, storms, evil ➢ Isis: goddess of magic and ambitious and clever women ➢ Horus: known as the avenger, god of courage ➢ Thoth: god of knowledge Technology sails 365 day calendar with leap years- the solar year and man-made calendar do not always match up Papyrus and ink - paper that is easy to write on and roll up First ox drawn plows Culture Cats- Snakes, mice, and rats were a threat to the Egyptian grain storage. The Egyptians learned that cats eat these animals and they began to leave food out to attract the cats. Eventually, the cats were welcomed into houses. It was believed that if you saw a cat in your dream you would have a good harvest. They believed that only a pharaoh had a high enough status to own a cat an harming a cat was considered treason. Embalming- First, the brain was removed through the nose. The heart was left in place while the rest of the organs were liquified using cedar oil. The body was flushed with water and left in natron, a salt, to be dried up. Then the body was mummified Ba and Ka-The ka was a spirit that left the body once death occured. The body was put through an embalming process to give the ka a place to live. The ba was part of the soul that could travel between the living and the dead. Art Works Cited http://www.pbs.org/empires/egypt/newkingdom/resources.html http://www.historymuseum.ca/splash http://www.pbs.org/empires/egypt/special/hieroglyphs/hieroglyphs_spell_results.php http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyperus_papyrus http://www.touregypt.net/egypt-info/magazine-mag05012001-magf4a.htm http://www.history.com/topics/ancient-history/the-egyptian-pyramids http://www.dipity.com/ http://www.ancient-egypt-online.com/ancient-egyptian-inventions.html http://www.history.com/shows/mankind-the-story-of-all-of-us/interactives/history-of-pyramids-infographic http://www.smithsonianmag.com/ist/?next=/history/the-queen-who-would-be-king-130328511/ http://www.kidzworld.com/article/1074-egypt-ancient-paper-papyrus http://www.kidsgen.com/ancient_egypt/daily_life.htm http://www.gotravel24.com/world/leap-year-facts-and-traditions http://www.infoniac.com/science/top-10-inventions-of-ancient-egypt.html http://www.omniglot.com/writing/coptic.htm Works Cited http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/265021/hieroglyphic-writing http://ss6shms.pbworks.com/w/page/24556952/Ancient%20Egypt http://myweb.usf.edu/~liottan/theegyptiansoul.html http://www.rickriordan.com/my-books/kane-chronicles/explore-egyptian-mythology/the-egyptian-gods.aspx http://www.mummies2pyramids.info/geography-cities/geography-cities-index.htm http://www.gks.uk.com/Horus-falcon-god/ http://www.uh.edu/engines/epi1502.htm http://www.iranpoliticsclub.net/authors/queen-nefertari/index.htm http://www.historyonthenet.com/egyptians/housing.htm http://looklex.com/e.o/egypt.ancient.life_styles.htm https://www.google.com/url? sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&docid=zBMmkxl6BH32hM&tbnid=Gjf6Gy2XILrsAM: &ved=0CAYQjB0&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.examiner.com%2Farticle%2Fgender-representation-ancient-egyptian-tombart&ei=iNsqVJ3bA8fCggTWo4DoDw&bvm=bv.76477589,d.cWc&psig=AFQjCNEPb_J-BvwnFixtCcDHJYDqsFQR8w&ust=1412181106316710 https://www.google.com/url? sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&docid=DDXGjjvWPzLPXM&tbnid=OcYH6JHfWb33TM: &ved=0CAYQjB0&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.tuttartpitturasculturapoesiamusica.com%2F2010%2F10%2Fancient-egypt. html&ei=yNsqVNjiFojCggSP6oFI&bvm=bv.76477589,d.cWc&psig=AFQjCNEPb_J-BvwnFixtCcDHJYDqsFQR8w&ust=1412181106316710