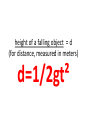* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Freefall and Newton`s 2nd Law ppt
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
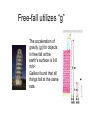
9 second freefall… video How fast is it going at the bottom? How tall is it? Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion F=ma If the same force acts on two different objects with different masses, how does the object’s acceleration (movement away) compare? Thinking about force change • If the force acting on an object goes up, and the mass doesn’t change, how does the acceleration change? If the same force acts on two different objects with different masses, how does the object’s acceleration (movement away) compare? F=ma Thinking about force change F=ma • If the force acting on an object goes up, and the mass doesn’t change, how does the acceleration change? • F = force – Measured in newtons (N) • m = mass units – Measured in kilograms (kg) • a = acceleration – Measured in meters per second per second (m/s²) Multiple forces can be exerted on an object at the same time • acceleration = change in velocity over time What is acceleration ? a= 𝑣2 − 𝑣1 𝑡 or a = Δ𝑣 𝑡 Apply Newton’s 2nd Law to Physics of kicking field goals Large asteroid impact simulation What would happen if you jumped into a well that went all the way through Earth? See answer in video Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion (F=ma) describes falling and weight (Fg = mag) • Fg = mag (or W=mg or F = mg) Weight is applied Newton’s 2nd – Fg = force due to gravity ( or W=weight) – ag (or g) = acceleration due to gravity • always = 9.8 m/s2 on Earth • Does a big guy or little guy fall faster when bungee jumping? • Fg = mag (or W=mg or F = mg) Weight is applied Newton’s 2nd – Fg = force due to gravity ( or W=weight) – ag (or g) = acceleration due to gravity • always = 9.8 m/s2 on Earth • Does a big guy or little guy fall faster when bungee jumping? They fall at the same speed, as mass is irrelevant to freefall speed Which would fall faster without air resistance, feathers or a bowling ball? video Air Resistance and free-fall • In air… – A stone falls faster than a feather • Air resistance affects stone less • In a vacuum – A stone and a feather will fall at the same speed. Free-fall utilizes “g” The acceleration of gravity (g) for objects in free fall at the earth's surface is 9.8 m/s2. Galileo found that all things fall at the same rate. Which would land first, a bullet fired or a bullet dropped? • Each bullet shows its position at seconds 0, 0.1, 0.2,and 0.3 Free-fall The rate of falling increases by 9.8 m/s every second. Height = ½ gt2 (Height is abbreviated either “y” or “d”) For example: ½ (9.8 )12 = 4.9 m ½(9.8)22 = 19.6 m ½ (9.8)32 = 44.1 m ½ (9.8)42 = 78.4 m Free-fall A ball thrown horizontally will fall at the same rate as a ball dropped directly. Its velocity can be calculated by multiplying the time in seconds by “g”. v=gt Free-fall A ball is thrown up from a rooftop 1. When would the velocity be the highest? 2. When is the vertical velocity = 0 m/s? 3. At what two points are the velocities equal? • What does this show? Projectile motion path shape An object thrown upward at an angle to the ground follows a curved path called a parabola. What do you notice about this shape? Air Resistance and free-fall – A person in free fall reaches a terminal velocity of around 54 m/s (about 130 mi./hr.) – With a parachute, terminal velocity is only 6.3 m/s Allows for a safe landing -the terminal velocity for a cat is 60 mi./hr. Air Resistance • Ideal angle for a projectile – In a vacuum, maximum distance is at an angle of 45o – With air resistance (real world), angle is less • Baseball will go furthest hit at an angle of around 40o, a soccer ball at about 33o 9 second freefall… video How fast is it going at the bottom? How tall is it? height of a falling object = d (for distance, measured in meters) d=1/2gt² SOLVE: How fast is it going at the bottom? How tall is it? Falling from Space Joe Kittenger • In the context of Theory of Relativity https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MQ7N6VYKJ8 Felix Baumgartner • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dYw4me RWGd4 • 8 min, RedBull • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FHtvDA0 W34I – 2 min., With mission control