* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrocardiography (ECG)
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
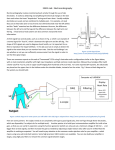
Lab-2- Anatomy and physiology 1 Electrocardiography ECG(EKG) Electrocardiography (ECG):-the machine which recorded the electrical activities of the heart on moving strip of paper by amplify electrical signals from the heart Purpose : ECG help in diagnosis of the following :1- Primary induction abnormalities 2- Electrolytes imbalance 3-Heart attack (Myocardial infarction) The electrocardiography assists in the diagnosis of specific cardiac abnormalities by detecting transmission of electrical impulses through the heart’s conductive tissues. This is accomplished by means of leads (or electrodes), attached to a patient’s limbs and chest, which transmit electrical impulses to the recording device. Different types of ECGs can be referred to by the number of leads that are recorded, for example 3-lead, 5-lead or 12-lead ECGs (sometimes simply "a 12-lead"). A 12-lead ECG is one in which 12 different electrical signals are recorded at approximately the same time and will often be used as a one-off recording of an ECG, traditionally printed out as a paper copy. 1. Of the 12 leads, the 4 limbs electrodes provide six leads( I,II,III, aVF, aVR, and aVL) measure electrical activity in the vertical plane. 2. Lab-2- Anatomy and physiology 2 2. While the six precordial electrodes provide six leads( V1,V2,V3,V4,V5, and V6) through the horizontal plane of the chest, which help determine the extent and location of myocardial damage. The precordial leads, designated as leads V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6, are placed at different angles in specific regions of the chest to register cardiac electrical activity in the horizontal plane and to reveal valuable information about specific regions of the heart. As shown above, the precordial leads are placed on the anterior chest in the following manner: V1 - is placed on the fourth intercostal space at the right sternal border V2 - is placed on the fourth intercostal space at the left sternal border V3 - is placed halfway between V2 and V4 V4 - is placed on the fifth intercostal space at the left midclavicular line V5 - is placed on the same level as V4 at the left anterior axillary line V6 - is placed on the same level as V4 at the left midaxillary line The precordial leads are also classified based on the region of the heart they are monitoring: V1 and V2 are called the septal leads. Electrical activity of the inter-ventricular septum is best measured in these leads. V3 and V4 are called the anterior leads. Electrical activity of the anterior (front) wall of the left ventricle is best measured in these leads. V5 and V6 are called the left precordial or lateral precordial leads. Electrical activity of the lateral (left) wall of the left ventricle is best measured in these leads (together with leads I and aVL). Lab-2- Anatomy and physiology 3 Each of the different electrodes (the six limb leads and the six precordial leads) monitors heart activity from its own specific angle and position. As a result specific areas of the heart are best analyzed through a particular set of leads.