* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DB2 Stored Procedure Introduction Unit objectives
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
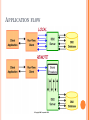
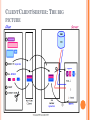
DB2 STORED PROCEDURE INTRODUCTION UNIT OBJECTIVES After completing this unit, you should be able to: Describe a stored procedure Determine when a stored procedure should be used Describe execution flow using stored procedures List DB2 stored procedure design and general tips WHAT IS A STORED PROCEDURE? A Stored Procedure: Is an executable program under control of the DB2 server Is invoked via the SQL CALL statement May contain business logic May be invoked locally or remotely May receive or pass parameters May produce result sets WHEN TO USE A STORED PROCEDURE Stored procedures may be justified when: The application's performance expectations are not being met There are a large number of clients to which application code is distributed. The client application generates relatively heavy database activity, but involves little user interaction. The client application code changes frequently. The access to the client application code needs to be controlled. The client application executes many SQL statements. CONSIDERATIONS WHEN USING STORED PROCEDURES Stored procedures are incorporated by: Determining client portion of application Thin client? Selecting stored procedure server Developing stored procedure Determining calling parameters Selecting programming language / SQL PL, PL SQL / IBM DB2 Data Studio Developer / CLP, Command Editor, Text Editor Defining SP to server Coding and testing APPLICATION FLOW CLIENTCLIENT/SERVER: THE BIG PICTURE SERVER PROCEDURE: DESIGN/GENERAL TIPS Consider the cost of invoking a stored procedure versus the cost of network transmission for a distributed application. Stored procedures run in background.–Do not use the standard I/O streams No commands to terminate current process. Overloading stored procedures restricted to parameter subsets. SQL limited by stored procedure CREATE parameters. UNIT SUMMARY Describe a stored procedure Determine when a stored procedure should be used Describe execution flow using stored procedures List DB2 stored procedure design and general tips