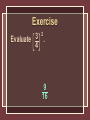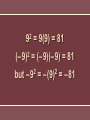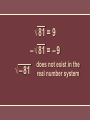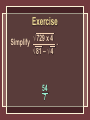* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Exercise Evaluate 32. 9 Exercise Evaluate (3 + 4)2. 49 Exercise Evaluate 32 + 42. 25 Exercise Evaluate 3 4 2 . 9 16 Exercise 2 3 Evaluate 2 . 4 9 16 Square Root The square root of x is a number whose product when multiplied by itself is x. 2 9 2 (– 9) = 9(9) = 81 = (– 9)(– 9) = 81 but – 92 = – (9)2 = – 81 √ 81 = 9 – √ 81 = – 9 √ – 81 does not exist in the real number system Example 1 Find √ 25 . 5 Example 1 Find – √ 49 . –7 Example State whether √ 144 is an integer, real, or not real. integer Example State whether √ 132 is an integer, real, or not real. real Example State whether √ –36 is an integer, real, or not real. not real 12 = 1 62 = 36 112 = 121 162 = 256 22 = 4 72 = 49 122 = 144 172 = 289 32 = 9 82 = 64 132 = 169 182 = 324 42 = 16 92 = 81 142 = 196 192 = 361 52 = 25 102 = 100 152 = 225 202 = 400 These are called “perfect squares.” 4 √ 16 = 4 = 1 rational number If x is not a perfect square then √ x is an irrational number. √ 5 is 2.236067977… You can estimate √ x by finding the two perfect squares between which x lies. Example 2 Between what two consecutive integers does √ 32 lie? 25 < 32 < 36 √ 25 < √ 32 < √ 36 5 < √ 32 < 6 √ 32 is between 5 and 6. Guess and Check Method:√ 19 16 < 19 < 25 √ 16 < √ 19 < √ 25 4 < √ 19 < 5 Estimate √ 19 ≈ 4.2 4.22 = 17.64 Estimate √ 19 ≈ 4.3 4.32 = 18.49 Estimate √ 19 ≈ 4.4 4.42 = 19.36 4.3 < √ 19 < 4.4 and √ 19 ≈ 4.4 Example 3 Estimate √ 47 to the nearest tenth. 36 < 47 < 49 √ 36 < √ 47 < √ 49 6 < √ 47 < 7 Estimate √ 47 to the nearest tenth. 6.92 = 47.61 0.61 greater than 47 6.82 = 46.24 0.76 less than 47 √ 47 ≈ 6.9 Example Order the following numbers from smallest to largest using the < symbol: 11.7, 11.5, √ 135, √ 139. 11.5 < √ 135 < 11.7 < √ 139 Example Determine what integers a2 lies between if a is any single-digit integer. 0 and 100 Example Determine what integers a2 lies between if a is any twodigit integer. 100 and 10,000 Example Estimate √ 53 by finding the two consecutive integers it lies between. 7 and 8 Example Estimate √ 53 by finding its decimal approximation to the nearest integer. 7 Example Estimate √ 53 by finding its decimal approximation to the nearest tenth. 7.3 Example Estimate √ 53 by finding its decimal approximation to the nearest hundredth. 7.28 √x + √y Simplify each square root before adding. √x + y Simplify by taking the square root after adding. Example 4 Simplify √ 64 + √ 25. √ 64 + √ 25 = 8 + 5 = 13 Example 4 Simplify √ 72 – 23. √ 72 – 23 = √ 49 =7 Order of Operations 1. Symbols of Grouping— evaluate quantities within symbols of grouping first. 2. Exponents and radicals— evaluate a term with an exponent or square root before performing other operations. Order of Operations 3. Multiplication and division—perform these operations in order from left to right. 4. Addition and subtraction— perform these operations last, in order from left to right. Example 5 Simplify –4 √ 116 – 35. – 4 √ 116 – 35 = –4 √ 81 = –4(9) = –36 Example Simplify 2 √ 80 + 64. 24 Example Simplify 3 √ 25 – 2 √ 64. –1 Example 3( √ 121 + √ 81) Simplify . 4 √ 100 – 64 5 2 Exercise √ 729 x 4 Simplify . √ 81 – √ 4 54 7