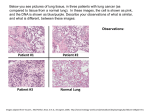
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 05 Introduction to Splanchnology. General anatomy of the dig
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Large intestine wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Respiratory system wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
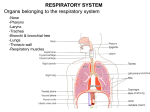
Introductio to: Splanchnology Composition: Alimentary system 消化系统 Respiratory system 呼吸系统 Urinary system 泌尿系统 Reproductive system 生殖系统 Characters of viscera Most of viscera organs lies in the thoracic, abdominal and pelvis cavities All of then communicate with external environment through some orifices or channels Reference lines of thorax Anterior median line Sternal line Midclavicular line Parasternal line Anterior axillary line Post axillary line Midaxillary line Scapular line Posterior median line The abdominal regions Nine regions Left and right hypochondriac region, epigastric region L . and R. lateral regions of abdomen, umbilical region L. and R. inguinal region, pubic region Four quadrants Left and right upper quadrants Left and right lower quadrants The Respiratory System Composition Respiratory tract Nose Pharynx upper respiratory tract Larynx Trachea lower respiratory tract Bronchi Lungs-paired organs of respiration Function: supply the body with oxygen and to get rid of excess carbon dioxide resulting from cell metabolism The Nose 鼻 External nose: Root of nose Back of nose Apex of nose Alae of nasi Nasal cavity –divided into two halves by nasal septum Two parts: Divided by limen nasi 鼻阈 Nasal vestibule Proper nasal cavity Boundaries Roof-cribriform plate of ethmoid Floor-hard palate Medial wall-nasal septum Lateral wall Nasal conchae: superior, middle and inferior Nasal meatus: superor, middle and inferior Sphenoethmoidal recess Remove the middle nasal conchae Semilunar hiatus 半月裂孔 Ethmoidal infundibulum 筛漏斗 Ethmoidal bulla 筛泡 Mucous membrane of nose Olfactory region嗅区: located upper nasal cavity, above superior, nasal conchae,contains olfactory cells Respiratory region 呼吸区: its function is to warm, moisten, and clean the inspired air The paranasal sinuses and their site of drainage into the nose Name of sinus Site of drainage Frontal sinus Middle meatus via infundibulum Maxillary sinus Middle meatus through semilunar hiatus Sphenoid sinus Sphenoethmoidal recess Ethmoidal sinuses anterior group middle group posterior group Middle meatus Middle meatus Superior nasal meatus Frontal sinus Ethmoidal sinuses Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus The Larynx 喉 Position-situated in the anterior part of the neck (below the hyoid bone), and extends from vertebral level of C4 to C6 Layngeal cartilages 喉软骨 Thyroid cartilage 甲状软骨 Shield-shaped cartilage Laryngeal prominence at base of thyroid notch Superior thyroid notch, superior and inferior cornua Cricoid cartilage 环状软骨 Complete ring of cartilage (shaped like a signet ring) Arch of cricoid cartilage-at level of C6 Larnina of cricoid cartilage Arytenoid 杓状软骨 Paired, pyramid shaped, articulate with lamina of cricoid cartilage Vocal process anteriorly, site of posterior attachment of vocal fold Muscular process Epiglottic cartilage 会厌软骨 leaf-shaped elastic cartilage situated behind the root of the tongue Laryngeal joints cricothyroid joint cricoarytenoid joint Laryngeal ligaments and membrane Thyrohyroid membrane 甲状舌骨膜-extending from hyoid bone to thyroid cartilage Quadrangular membrane 方形膜 Conus elasticus 弹性圆锥 Between epiglottic, thyroid and arytenoid cartilages Lower free border forms vestibular ligament 前庭韧带 Between arytenoids, thyroid, and cricoid cartilages Upper free border forms vocal ligament 声韧带 Median cricothyroid ligment 环甲正 中韧带:may be site of circothyrotomy during acute respiratory obstruction Cricotracheal ligament 环状软骨气管韧带-between cricoid cartilage and first ring of trachea Muscles of larynx Increasing tension on the vocal ligament-cricothyroid Decreasing tension on the vocal ligament-thyroarytenoid Opening the glottis-posterior cricoarytenoid Closing the glottis- cricoarytenoid Laryngeal cavity Aperture of larynx 喉口-bounded by upper border epiglottic cartilage, aryepiglottic folds and interarytenoid notch Structure features Two pairs of shelf like folds : Vestibular folds 前庭襞 Vocal folds 声襞 Two fissures Rima vestibulithe 前庭裂 Fissure of glottis 声门裂 Inter membranous part膜间部 -anterior 3/5, between vocalfolds Inter cartilagrnous part 软骨间部 -posterior 2/5, between arytenoids cartilages Three parts Laryngeal vestibule 喉前庭 Extends from the aperture of larynx to the rima vestibuli Tubercle of epiglottis 会厌结节 Intermedial cavity of larynx喉 中间腔 Extends from the level of the rima vestibuli to the level of the fissure of glottis Ventricle of larynx 喉室 -a small recess between vestibular and vocal folds on each side Infraglottic cavity 声门下腔 extends from the level of the vocal folds to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage The Trachea 气管 Position: extends from the lower border of cricoid cartilage to the level of sternal angle (between T4-T5 vertebrae) where it divides into right and left principal bronchi Structure features Consists of about 16-20 Cshaped incomplete tracheal cartilages for patency connected by smooth muscle and connective Carina of trachea 气管隆嵴 -ridge of cartilage at bifurcation into principal bronchi Bronchi 支气管 Right principal bronchus 右主支气管 Shorter, wider, and more vertical than the left , is about 2.5cm long, Leaves the extend line of the middle line of trachea at 22~25o angle Foreign bodies are therefore more likely to lodge in this bronchus or one of its branches Left principal bronchus 左主支气管 Narrower, longer, and more horizontal than the right is about 5cm long, leaves the extend line of the middle line o trachea at about 35~36o angle The Lungs 肺 Position: located in the thoracic cavity by both sides of mediastinum General features Cone-shaped, the right lung is shorter and broader, the left one is longer and narrower Apex of lung-rises 2 ~3 cm above the medial third of clavicle into neck Base-concave, related to diaphragm, also called diaphragmatic surface Costal surface-large, convex, related to thoracic wall Medial surface-concave, related to mediastinum and vertebrae Hilum of lung 肺门:area on medial surface where structures in root enter or leave lung Root of lung 肺根 Contents Principal bronchus Pulmonary artery and vein Nerves and lymphatics Surrounded by connective tissue Order of structures in the root of lung From before backward: V.A. B. From above downward: R.-B. A. V. L.-A. B. V. Borders Posterior-blunt Inferior- sharp Anterior-sharp cardiac notch心切迹 lingual in left lung 左肺小舌 Lobes and Fissure Right lung Two fissures : horizontal an oblique Three lobes : superior, middle, inferior Left lung One fissure : oblique Two lobes : superior and inferior Bronchial tree支气管树 Each principal bronchus divides into lobar bronchi (two on the left, three on the right), each of which supplies a lobe of lung. Each lobar bronchus then divided into segmental bronchi, which supply specific segments of the lung. Bronchopulmonary segments支气管肺段 Wedge shaped, with the base lying peripherally and the apex lying towards the root of lungs, ten in each lung Each with a segmental bronchus and branches of pulmonary artery The veins lie both in and between segments The Pleura 胸膜 General features Serous membranes forming closed sacs Two layers Visceral pleura-adheres to lung, continuous with parietal pleura at root of lung Parietal pleura-lines the thoracic cavity Two pleural layers continue with each other at root of lung forming closed potential space-pleural cavity 胸膜腔 Contains a small amount pleural fluid Subatmospheric pressure in it Named parts of parietal pleura Cupula of pleura 胸膜顶 -extends up into the neck, over the apex of lung, 2~3cm above the medial third of clavicle Costal pleura 肋胸膜 -lines the inner surface of the wall of the chest Mediastinal pleura 纵隔胸膜 Lines mediastinum Pulmonary ligament 肺韧带 -redundant pleura at root of lung, which extends downward, allows movement of structures forming root of lung Diaphragmatic pleura 膈胸膜- Lines diaphragm Pleura recesses 胸膜隐窝- potential spaces of pleural cavity which lungs are not occupied in quiet respiration Costodiaphragmatic recesse肋 膈隐窝-are the slit-like intervals between costal and diaphragmatic pleurae on each side, the lowest point of pleural cavity Costomediastinal recess 肋纵隔隐窝-on the left side between the mediastinal pleural and costal pleura The surface projection of lower border of lung and pleurae Lower border Midclavicular lines Midaxillary lines Sides of the vertebral column Lungs 6th rib 8th rib 10th rib Pleura 8th rib 10th rib 12th rib General anatomy of the Digestive System Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption Defecation include Overview of Digestive System Histological Organization Same basic arrangement of tissues from esophagus to anal canal Four layers (from innermost to outermost) Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Serosa Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials Peristalsis Coordinated motion of two muscular layers Circular muscles contract, then longitudinal muscles Segmentation Mixing of food Circular muscles in two areas contract Longitudinal muscles alternately contract & relax The Oral Cavity Structure Lined with stratified squamous epithelium Lips surround the opening Roof is formed from the hard & soft palate Tongue dominates the floor Functions Take in food Prepare food for digestion The Tongue Structure Skeletal muscle covered with mucosa The lingual frenulum connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth Surface Papillae Functions Maneuvers food Salivary Glands Found outside mouth Ducts carry saliva to mouth 3 pairs Parotid glands Submandibular glands Sublingual glands Saliva Functions Keeps mucous membranes moist Lubricates food Dissolves food Begins carbohydrate digestion 2 sets Deciduous (20) Permanent (32) Held in sockets Gingiva = gums Structure Crown Root Neck Composition Dentin Enamel Cementum Dental caries Wisdom teeth Teeth The Pharynx and Esophagus Food enters the esophagus from the pharynx The esophagus is a muscular tube behind the trachea Food is moved by peristalsis from the pharynx to the stomach Cardiac sphincter separates esophagus from stomach Stomach The Stomach Same 4 basic layers When the stomach is empty, the mucosa lies in large folds Rugae Pyloric sphincter separates stomach from small intestine Histology of the Stomach Mucosa is simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells Mucosa is folded to form gastric pits Gastric glands secrete gastric juice Gastric Gland Several kinds of cells produce substances that form gastric juice Mucus cells Chief cells Parietal cells Enteroendocrine cells Functions of the Stomach Mechanical Food reaches pylorus Chemical digestion Digestion of proteins Absorption digestion No food Water, electrolytes Some drugs Alcohol The Small Intestine About 18 feet long The duodenum About 8 inches long Common bile duct & pancreatic duct empty here The jejunum About 8 feet long Most digestion occurs here The ileum About 9.5 feet long Most absorption occurs here Ends in the ileocecal valve A Villus Functions of the Small Intestine Chyme is further broken down Proteins Carbohydrates Fats Most absorption is in the small intestine The Large Intestine (Colon) About 4.5 feet long Mesocolon supports Begins with the cecum Appendix is attached Ascending colon Transverse colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Colon connects to rectum Rectum connects to anal canal Empties to the exterior through the anus Histology and Functions of the Large Intestine Mucosa - simple columnar epithelium Completion of absorption Formation of feces Lots of mucus glands Expulsion of feces from the body Digestion in the Large Intestine Mechanical Regulated by the ileocecal valve Mixing and peristalsis Mass peristalsis Chemical Mucus secreted No enzymes Bacteria – prepare chyme for elimination Feces Formation & Defecation Chyme is now solid or semi-solid - feces Large intestine absorbs any more water and electrolytes from feces Defecation Mass peristalsis pushes fecal material into rectum Rectum stretches Defecation reflex Accessory Organs Liver Pancreas Gall bladder The Liver Performs many lifesustaining functions Location – under the diaphragm on the right Connected to the diaphragm by the falciform ligament Divided into lobes Right lobe Left lobe Caudate lobe Quadrate lobe Histology of the Liver Outside is a capsule Composed of tiny lobules Each lobule is surrounded by liver cells and sinusoids Hepatocytes Kupffer cells Bile ducts run between liver cells Functions of the Liver bile – the primary digestive function Produces Composition Water Bile salts Cholesterol Pigments Bilirubin Digestive function Emulsification of fats Other Functions of the Liver Absorbs and stores iron, vitamins A, D, E, B7, K Detoxifies toxins and hormones Metabolizes proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids Removes bacteria from the blood Produces plasma proteins Removes worn-out and damaged red blood cells The Gallbladder Location – underside of right lobe of liver Function – concentrate and store bile Collected from liver Hepatic ducts Adds bile to duodenum Cystic duct Common bile duct Gallstones The Pancreas Location – in the curvature of the duodenum Connected to the duodenum by the pancreatic duct Produces pancreatic juice Functions Exocrine - digestion of all nutrient groups Endocrine – control blood glucose level