* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lungs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
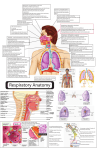
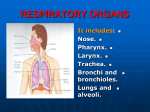
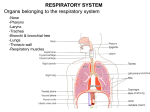
Splanchnology SHANDONG UNIVERSITY Liu Zhiyu Splanchnology Composition: Alimentary system Respiratory system Urinary system Reproductive system Characters of viscera Most of viscera organs lies in the thoracic, abdominal and pelvis cavities All of then communicate with external environment through some orifices or channels Reference lines of thorax Anterior median line Sternal line Midclavicular line Parasternal line ★ Reference lines of thorax Posterior median line Anteriorlary line Midaxillary line Posterior axillary line Scapular line The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Composition Respiratory tract upper respiratory tract lower respiratory tract Bronchi Lungs : paired organs of respiration Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Function of respiratory system : supply the body with oxygen and to get rid of excess carbon dioxide resulting from cell metabolism The Nose External nose Root of nose Back of nose Apex of nose Alae of nasi Nasal cavity Nasal cavity is divided into right and left halves by nasal septum. The septum is made up of the septal cartilage, the vertical plate of the ethmoid, and the vomer. Each nasal cavity extends from the nostril in front to the choanae behind. Nasal septum Nasal cavity Two parts: Divided by limen nasi Nasal vestibule Proper nasal cavity Boundaries of nasal cavity Roof-cribriform plate of ethmoid Floor-hard palate Medial wall-nasal septum Lateral wall ★ Superior, middle and inferior nasal conchae Superior, middle and inferior nasal meatus Sphenoethmoidal recess Nasal cavity Remove the middle nasal conchae Ethmoidal bulla Semilunar hiatus Ethmoidal infundibulum Nasal cavity Mucous membrane of nasal cavity The vestibule is lined by modified skin. Olfactory region : the area above superior nasal conchae is lined with olfactory mucous membrane which contains olfactory cells Respiratory region : the lower part of the nasal cavity is lined with respiratory mucous membrane. Its function is to warm, moisten, and clean the inspired air. ★The paranasal sinuses Name of sinus Site of drainage Frontal sinus Middle meatus via infundibulum Maxillary sinus Middle meatus through semilunar hiatus Sphenoid sinus Sphenoethmoidal recess Ethmoidal sinuses anterior group middle group posterior group Middle meatus Middle meatus Superior nasal meatus Frontal sinus Ethmoidal sinuses Sphenoid sinus Maxillary sinus The Larynx ★ Position-situated in the anterior part of the neck (below the hyoid bone), and extends from vertebral level of C3 to C6 The framework of the larynx is made up of cartilages, which connected by membranes and ligaments and moved by muscles. It is lines by mucous membrane. ★ Layngeal cartilages Thyroid cartilage Shield-shaped cartilage Laryngeal prominence Superior thyroid notch Superior and inferior cornua Cricoid cartilage Complete ring of cartilage (shaped like a signet ring) Arch of cricoid cartilage-at level of C6 Larnina of cricoid cartilage ★ Layngeal cartilages Arytenoid cartilage Paired, pyramid shaped, articulate with lamina of cricoid cartilage Vocal process anteriorly, site of posterior attachment of vocal fold Muscular process Epiglottic cartilage Leaf-shaped elastic cartilage Attached by its stalk to the thyroid cartilage Laryngeal joints Cricothyroid joint Cricoarytenoid joint Membranes and ligaments of larynx Thyrohyroid membrane -extending from hyoid bone to thyroid cartilage Membranes and ligaments of larynx Quadrangular membrane Between epiglottic, thyroid and arytenoid cartilages Lower free border forms vestibular ligament Conus elasticus Between arytenoids, thyroid, and cricoid cartilages Upper free border forms vocal ligament Median cricothyroid ligment may be site of circothyrotomy during acute respiratory obstruction Membranes and ligaments of larynx Quadrangular membrane Vocal ligament Vestibular ligament Conus elasticus Membranes and ligaments of larynx Cricotracheal ligament -between cricoid cartilage and first ring of trachea Muscles of larynx Tensing the vocal ligament-cricothyroid Cricothyroid Muscles of larynx Relaxing the vocal ligament-thyroarytenoid Thyroarytenoid Muscles of larynx Opening the glottis-posterior cricoarytenoid Posterior cricoarytenoid Muscles of larynx Closing the glottis- lateral cricoarytenoid Lateral cricoarytenoid Laryngeal cavity of larynx - bounded by upper border epiglottic cartilage, aryepiglottic folds and interarytenoid notch ★ Aperture ★ Laryngeal cavity Two pairs of shelf like folds : Vestibular folds Fixed fold on each side of the larynx Formed by mucous membrane covering the vestibular ligament and is pink in color Vocal folds Mobile fold on each side of the larynx. Formed by mucous membrane covering the vocal ligament and is white in color ★ Laryngeal cavity Two fissures Rima vestibuli Fissure of glottis The narrowest part of the laryngeal cavity Inter membranous part - anterior 3/5, between vocal-folds Intercartilaginous part - posterior 2/5, between arytenoids cartilages ★ Laryngeal cavity Three parts Laryngeal vestibule Extends from the aperture of larynx to the rima vestibuli Tubercle of epiglottis Intermedial cavity of larynx Extends from the level of the rima vestibuli to the level of the fissure of glottis Ventricle of larynx a small recess between vestibular and vocal folds on each side Infraglottic cavity extends from the level of the vocal folds to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage ★ The Trachea Position Extends from the lower border of cricoid cartilage to the level of sternal angle (between T4-T5 vertebrae) where it divides into right and left principal bronchi Structure features Consists of about 14-17 Cshaped incomplete tracheal cartilages Bifurcation of trachea Carina of trachea — ridge of cartilage at bifurcation ★ Bronchi Right principal bronchus Shorter, wider, and more vertical than the left About 2.5cm long, Leaves the extend line of the middle line of trachea at 22~25o angle Foreign bodies are therefore more likely to lodge in this bronchus or one of its branches Left principal bronchus Narrower, longer, and more horizontal than the right About 5cm long, leaves the extend line of the middle line o trachea at about 35~36o angle ★ The Lungs Position: Located in the thoracic cavity by both sides of mediastinum General features Cone-shaped, the right lung is shorter and broader, the left one is longer and narrower Apex of lung-projects upward into the neck for approximately 2.5 cm above the medial third of clavicle into neck Base-concave, sits on the diaphragm, also called diaphragmatic surface Costal surface-large, convex, related to thoracic wall ★ The Lungs Medial surface-concave, related to mediastinum Hilum of lung middle of medial surface, which is a depression where the bronchi, vessels, and nerves enter the lung to form the root Root of lung Contents Principal bronchus Pulmonary artery and vein Nerves and lymphatic vessels Surrounded by connective tissue Order of structures in the root of lung From before backward: V.A. B. From above downward: L.-A. B. V. R.-B. A. V. ★ The Lungs Borders Anterior-sharp Cardiac notch Lingual in left lung Posterior-blunt Inferior- sharp ★ The Lungs Lobes and Fissure Right lung Two fissures : horizontal and oblique Three lobes : superior, middle, inferior Left lung One fissure : oblique Two lobes : superior and inferior Bronchial tree Each principal bronchus divides into lobar bronchi (two on the left, three on the right), each of which supplies a lobe of lung. Each lobar bronchus then divided into segmental bronchi, which supply specific segments of the lung. Bronchopulmonary segments Bronchopulmonary segments are the anatomic, functional, and surgical units of the lungs. It is pyramidal in shape, with its apex toward the lung root, ten in each lung It has a segmental bronchus, a segmental artery, lymph vessels, and nerves. The segmental veins lie in the connective tissue between bronchopulmonary segments Because it is a structural unit, a diseased segment can be removed surgically. Bronchopulmonary segments Bronchogram showing the branching pattern of the trachea and bronchi of the right lung, in a slightly oblique anteroposterior view. In this procedure, a radiopaque contrast medium has been introduced into the respiratory tract to coat the walls of the respiratory passages ★ The Pleura General features Serous membranes forming closed sacs Two layers Visceral pleura - covers the outer surfaces of the lungs, and extends into the interlober fissures Parietal pleura -lines the thoracic wall and coves the diaphragm and the lateral surface of the mediastinum The Pleura Two pleural layers continue with each other at root of lung forming closed potential space- pleural cavity Contains a small amount of pleural fluid Subatmospheric pressure in it ★ Named parts of parietal pleura Cupula of pleura - extends up into the neck, over the apex of lung, 2.5cm above the medial third of clavicle Costal pleura -lines the inner surface of the wall of the chest Mediastinal pleura Lines mediastinum Pulmonary ligament - redundant pleura at root of lung, which extends downward, allows movement of structures forming root of lung Diaphragmatic pleura - Lines diaphragm Pleura recesses Potential spaces of pleural cavity which lungs are not occupied in quiet respiration Costodiaphragmatic recesse-are the slit-like space between costal and diaphragmatic pleurae on each side, the lowest area of pleural cavity into which the lungs expand during deep inspiration. Costomediastinal recess -on the left side between the mediastinal pleural and costal pleura ★ Surface markings of lower border of the lung and pleura Lower border Midclavicular lines Midaxillary Scapular lines line Sides of the vertebral column Lungs 6th rib 8th rib 10th rib T11 Pleura 8th rib 10th rib 11th rib T12 Thoracentesis