* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic history - Kenton County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
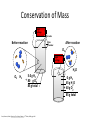
Atomic history • Democritus first person to use the term atom in 400 B.C. • Democritus defined the atom as being indivisible • Conservation of mass: mass cannot be created or destroyed during chemical and physical changes. Conservation of Mass High voltage electrodes Before reaction After reaction glass chamber O2 High voltage H2O O2 H2 5.0 g H2 + 80 g O2 85 g total 0 g H2 45 g H2O + 40 g O2 85 g total Dorin, Demmin, Gabel, Chemistry The Study of Matter , 3rd Edition, 1990, page 204 Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are identical and atoms of different elements are different 2. Atoms 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in wholenumber ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are separated, combined, and rearranged. Major discoveries • Thomson conducted the cathode ray experiment • Thomson concluded that cathode rays were composed of identical negatively charged particles • Millikan concluded that electrons are present in atoms of all elements. • Rutherford conducted the gold foil experiment • Rutherford discovered the nucleus • Goldstein discovered the proton • Chadwick discovered the neutron