* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Script for animation
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
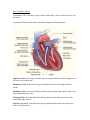
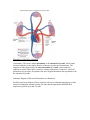
The Circulatory System Commentary: The circulatory system consists of the heart, a series of blood vessels, and the blood Anatomical Structure of the Heart: Schematic Diagram of Pumping Heart Superior Vena Cava: Large vein that brings de-oxygenated blood from the upper part of the body to the right atrium Pulmonary Veins: Bring fresh oxygenated blood from each of the lungs to the left atrium Pulmonary Valve: Prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle after it has entered the pulmonary artery Tricuspid Valve: Prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium after it has entered the right ventricle Inferior Vena Cava: Vein that brings deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body to the right atrium Aorta: Brings oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the body Pulmonary Arteries: Bring oxygen-poor blood to the right or left lung Aortic Valve: Prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle after it has entered the aorta Mitral Valve: Prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium after it has entered the left ventricle Additional Labels on the Diagram (w/o descriptions): Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Septum Blood Circulation throughout the Heart and the rest of the Body Commentary: The circulatory system is divided into two pathways. The pathway that carries blood between the heart and the lungs is the pulmonary circulation. The pathway that carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body is the systemic circulation. Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to other parts of the body Veins: Blood vessels that bring blood back to the heart from other parts of the body Schematic Diagram of Blood Circulation: Possibly same heart diagram of basic heart as previous animation but with animation of deoxygenated(blue)/oxygenated(red) blood flowing through the heart. Stimulation of the Heart: Heartbeat Commentary: The heart’s natural pacemaker is the sinoatrial (SA) node, which sends electrical impulses to the cardiac muscles of the atria to cause atrial contraction. The impulses are then picked up by the atrioventricular (AV) node, which sends the impulses to muscle fibers in the ventricles, causing contraction of ventricles. Artificial pacemakers are necessary for patients who have irregular heartbeats due to problems with the sinoatrial (SA) node. Schematic diagram of Electrical Stimulation in a Heartbeat: Possibly same heart diagram of basic heart but with a new animation popping up to show arrows of stimulation coming from the SA node into the right atrium and then these impulses are picked up by the AV node.