* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Experiment 3.3 Thomson Experiment Aim To use a computer
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetorotational instability wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
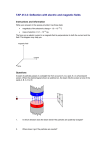
Experiment 3.3 Thomson Experiment Aim To use a computer simulation to analyse Thomson’s experiment. http://www.hscphysics.edu.au/resource/template.swf Algebra practice 1. Equate the equation for electric force with the equation for magnetic force to derive an expression for the velocity of a charged particle 2. Equate the equation for magnetic force with the equation for centripetal force amd to derive an expression for the charge to mass ratio for a charged particle 3. Substitute the first derived expression into the second derived expression and simplify for an expression for the charge to mass ratio for a charged particle. In this step Magnetic field and electric field were both on and adjusted until the beam shows zero net deflection. Record the magnetic field produced by the coils ................................. = ........................................ T Record the voltage applied to the parallel plates. ..................................... Calculate the magnitude of the electric field ..................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................... When there is zero net deflection, the electric force on the beam in one direction is equal to the magnetic force on the beam in the opposite direction. Therefore we can equate the two forces. Equate the electric force with the magnetic force and determine the velocity of the particles. ..................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................... In this step The Electric field was left on, the magnetic field turned off and the radius of beam path measured. Record the radius of the beam ............................... The magnetic force on the beam is providing a centripetal force for the circular path. Therefore we can equate the magnetic force with the centripetal force on the beam. Equate the equation for magnetic force with the equation for centripetal force and rearrange so that q/m is on one side of the equation ..................................................................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................................................................... Substitute value from the experiment into this expression to calculate the charge to mass ration for an electron Value from above v= ....................................., E = ..........................................., B= ............................................ ............................................................................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................................................................ Use your data sheet to calculate the q/m ratio of an electron to comment on the validity of the sumilation result. ........................................................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................................................................ Calculate the charge to mass ratio for the following results in the same experiment as above. (show working) For (c) you are to use the simulation at home to cllect a set of values and calculate the charge to mass ration for an electron. (a) (b) (c) Voltage applied to plates (V) 11.8 55 Magnetic field applied (T) 183 835 Radius of path (m) 0.412 .090